Inflammation in Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 40141426
- PMCID: PMC11943298
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26062785
Inflammation in Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
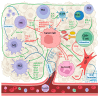
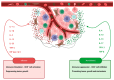
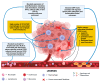
Inflammation appears to play a crucial role in the development and progression of penile cancer (PeCa). Two molecular pathways of PeCa are currently described: HPV-dependent and HPV-independent. The tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) of PeCa is characterized by the presence of tumor-associated macrophages, cancer-associated fibroblasts, and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. The components of the TIME produce pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, which have been found to be overexpressed in PeCa tissues and are associated with tumor progression and unfavorable prognoses. Additionally, the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway and secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1) have been implicated in PeCa pathogenesis. Elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) have been identified as potential prognostic biomarkers in PeCa. This overview presents the complex contribution of the inflammatory process and collates projects aimed at modulating TIME in PeCa.
Keywords: HPV; cytokines; inflammation; penile cancer; tumor immune microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Engelsgjerd J.S., Leslie S.W., LaGrange C.A. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. Penile Cancer and Penile Intraepithelial Neoplasia. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

