Flaxseed in Diet: A Comprehensive Look at Pros and Cons
- PMID: 40142110
- PMCID: PMC11945857
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30061335
Flaxseed in Diet: A Comprehensive Look at Pros and Cons
Abstract
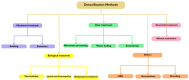
Flaxseeds, which have been consumed for thousands of years, have recently gained increasing popularity due to their rich composition, including omega-3 fatty acids, lignans, proteins, and fibers. These components are strongly associated with various health benefits, such as improving cardiovascular health, preventing certain types of cancer, controlling diabetes, promoting gastro-intestinal well-being, and aiding in weight management. This monograph explores the role of flaxseeds in nutrition, as well as their potential risks. Despite their numerous health benefits, flaxseeds also represent concerns due to excessive consumption and possible contamination, particularly from cyanogenic glycosides. Therefore, the levels of these compounds must be controlled, and this monograph also analyzes the available methods to detect and reduce these contaminants, ensuring the safety of flaxseed and flaxseed products consumers. Flaxseed is considered a valuable addition when incorporated into the diet, but it is necessary to continue research and promote technological improvements to maximize their benefits and minimize their risks.
Keywords: benefits; cyanogenic glycosides; determination methods; detoxification methods; diet; flaxseed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hall C., 3rd, Tulbek M.C., Xu Y. Flaxseed. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2006;51:1–97. - PubMed
-
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency The Biology of Linum usitatissimum L. (Flax) [(accessed on 28 February 2024)]. Available online: https://inspection.canada.ca/en/plant-varieties/plants-novel-traits/appl....
-
- Kauser S., Hussain A., Ashraf S., Fatima G., Ambreen, Javaria S., Abideen Z.U., Kabir K., Yaqub S., Akram S., et al. Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum); Phytochemistry, Pharmacological Characteristics and Functional Food Applications. Food Chem. Adv. 2024;4:100573. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2023.100573. - DOI
-
- Fu Y.-B. Genetic Evidence for Early Flax Domestication with Capsular Dehiscence. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2011;58:1119–1128. doi: 10.1007/s10722-010-9650-9. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

