Evaluating Interlaboratory Variability in Wastewater-Based COVID-19 Surveillance
- PMID: 40142419
- PMCID: PMC11945948
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13030526
Evaluating Interlaboratory Variability in Wastewater-Based COVID-19 Surveillance
Abstract
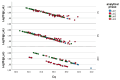
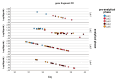
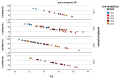
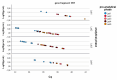
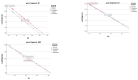
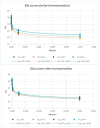
Wastewater-based environmental surveillance enables the monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 dynamics within populations, offering critical epidemiological insights. Numerous workflows for tracking SARS-CoV-2 have been developed globally, underscoring the need for interlaboratory comparisons to ensure data consistency and comparability. An inter-calibration test was conducted among laboratories within the network monitoring SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater samples across the Lombardy region (Italy). The test aimed to evaluate data reliability and identify potential sources of variability using robust statistical approaches. Three wastewater samples were analyzed in parallel by four laboratories using identical pre-analytical (PEG-8000-based centrifugation) and analytical processes (qPCR targeting N1/N3 and Orf-1ab). A two-way ANOVA framework within Generalized Linear Models was applied, and multiple pairwise comparisons among laboratories were performed using the Bonferroni post hoc test. The statistical analysis revealed that the primary source of variability in the results was associated with the analytical phase. This variability was likely influenced by differences in the standard curves used by the laboratories to quantify SARS-CoV-2 concentrations, as well as the size of the wastewater treatment plants. The findings of this study highlight the importance of interlaboratory testing in verifying the consistency of analytical determinations and in identifying the key sources of variation.
Keywords: SARS-CoV2; detection methods; generalized linear models; interlaboratory ring test; wastewater environmental surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Fabio Ferrari, Maria Giovanna Guiso, Antonino Martines and Desdemona Olivawas were employed by the company CAP Holding Spa. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report. [(accessed on 10 February 2025)]. Available online: http://covid19.who.int.
-
- Wilhelm A., Schoth J., Meinert-Berning C., Agrawal S., Bastian D., Orschler L., Ciesek S., Teichgräber B., Wintgens T., Lackner S., et al. Wastewater Surveillance Allows Early Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2022;846:157375. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157375. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hillary L.S., Farkas K., Maher K.H., Lucaci A., Thorpe J., Distaso M.A., Gaze W.H., Paterson S., Burke T., Connor T.R., et al. Monitoring SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater to evaluate the success of lockdown measures for controlling COVID-19 in the UK. Water Res. 2021;200:117214. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117214. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

