Topical Heparin and Heparinoid-Containing Products as Treatments for Venous Disorders: Compounds, Effects, Clinical Implications, and Recommendations
- PMID: 40142670
- PMCID: PMC11942652
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14061859
Topical Heparin and Heparinoid-Containing Products as Treatments for Venous Disorders: Compounds, Effects, Clinical Implications, and Recommendations
Abstract
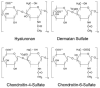
Background: Although considerable data are available on oral venoactive drugs, very little information has been published on the types and outcomes of topical treatments for venous disease (VD). This comprehensive review assesses the efficacy and safety of topical heparin and heparinoid-containing products (HCPs) for VD treatment. Methods: This narrative review adhered to established methodologies and standards, utilizing the Scale for the Assessment of Narrative Review Articles (SANRA) for quality assessment. A comprehensive literature search was conducted across MEDLINE (PubMed), Scopus, and Web of Science, covering publications from January 1, 1950, to December 1, 2024. Findings were presented in a narrative format, following structured recommendations to ensure clarity and coherence. Results: Topical heparin and HCPs provide anticoagulation, enhance microcirculation, and regulate skin permeability, with effects influenced by the concentration and formulation. While they effectively improve skin microcirculation in healthy individuals, research on their intracellular effects is limited. Mucopolysaccharide polysulfate (MPS) in heparinoids offers similar vascular benefits and promotes antithrombotic and anti-inflammatory actions. Moisture and gentle abrasion enhance heparin absorption. Topical heparin and HCPs effectively treat superficial vein thrombosis (SVT) and varicose veins (VVs). Products like Hirudoid significantly alleviate SVT symptoms, including pain and swelling. Clinical trials demonstrate substantial symptom improvement with heparin gel (1000 IU/g). For varicose veins, Xioglican cream stabilizes symptoms and improves quality of life, while other formulations like Essaven Gel and Venoruton enhance microcirculation. Conclusions: Managing VD with topical treatments is complicated by the outdated literature and inconsistent methodologies. There is a clear need for systematic research to establish guidelines on the administration, dosage, and frequency of topical treatments. The recommendations in this review aim to provide a foundation for future studies to improve the management of SVT and VVs disease.
Keywords: chronic venous disease; glycosaminoglycan; heparin; topical treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
D.B. serves as a consultant for STADA Arzneimittel AG., C.P., I.D., and G.A. certify that there are no conflicts of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Gianesini S., Obi A., Onida S., Baccellieri D., Bissacco D., Borsuk D., Campisi C., Campisi C.C., Cavezzi A., Chi Y.W., et al. Global guidelines trends and controversies in lower limb venous and lymphatic disease: Narrative literature revision and experts’ opinions following the vWINter international meeting in Phlebology, Lymphology & Aesthetics, 23–25 January 2019. Phlebology. 2019;34((Suppl. S1)):4–66. - PubMed
-
- Ortega M.A., Fraile-Martínez O., García-Montero C., Álvarez-Mon M.A., Chaowen C., Ruiz-Grande F., Pekarek L., Monserrat J., Asúnsolo A., García-Honduvilla N., et al. Understanding Chronic Venous Disease: A Critical Overview of Its Pathophysiology and Medical Management. J. Clin. Med. 2021;10:3239. doi: 10.3390/jcm10153239. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Green D. The Heparins: Basic and Clinical Aspects. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020. 214p
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources