Open Source Repurposing Reveals Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Activity of Diphenylureas
- PMID: 40143313
- PMCID: PMC11945542
- DOI: 10.3390/v17030385
Open Source Repurposing Reveals Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Activity of Diphenylureas
Abstract
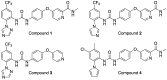
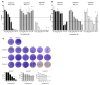
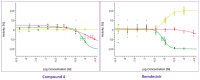
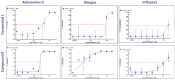
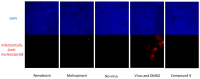
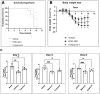
The pandemic threat from newly emerging viral diseases constitutes a major unsolved issue for global health. Antiviral therapy can play an important role in treating and preventing the spread of unprecedented viral infections. A repository of compounds exhibiting broad-spectrum antiviral activity against a series of different viral families would be an invaluable asset to be prepared for future pandemic threats. Utilizing an open innovation crowd-sourcing paradigm, we were able to identify a compound class of diphenylureas that exhibits in vitro antiviral activity against multiple viruses, including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), adenovirus, dengue virus, herpes, and influenza viruses. Compound 4 among the series exhibits strong activity against dengue virus, a growing global health problem with high medical need and no approved antiviral drug. The compounds are active against SARS-CoV-2 in a primary human stem cell-based mucociliary airway epithelium model and also active in vivo, as shown in a murine SARS-CoV-2 infection model. These results demonstrate the potential of the chemical class as antivirals on the one hand and the power of open innovation, crowd-sourcing, and repurposing on the other hand.
Keywords: broadband antiviral compounds; pandemic preparedness; repurposing.
Conflict of interest statement
U. Betz, N. Beier, R. Garces, and S. Lindemann are employees of Merck Group. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Physical interventions to interrupt or reduce the spread of respiratory viruses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 30;1(1):CD006207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006207.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36715243 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro antiviral activities of thymol and Limonin against influenza a viruses and SARS-CoV-2.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22587. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06967-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596436 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of experimental evidence for antiviral effects of ivermectin and an in silico analysis of ivermectin's possible mode of action against SARS-CoV-2.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;35(2):260-276. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12644. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33427370 Free PMC article.
-
Imiquimod, a Promising Broad-Spectrum Antiviral, Prevents SARS-CoV-2 and Canine Coronavirus Multiplication Through the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway.Viruses. 2025 May 31;17(6):801. doi: 10.3390/v17060801. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40573392 Free PMC article.
-
Measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5:CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029.pub2. PMID: 35037252 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

