La Jolla Virus: The Pathology and Transmission in Its Host Drosophila suzukii
- PMID: 40143335
- PMCID: PMC11945923
- DOI: 10.3390/v17030408
La Jolla Virus: The Pathology and Transmission in Its Host Drosophila suzukii
Abstract
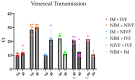
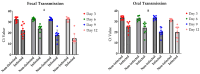
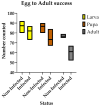
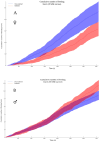
Drosophila suzukii, commonly known as spotted-wing drosophila, has emerged as a highly destructive pest in global fruit and wine production. The effectiveness of chemical control is significantly compromised by rapid resistance development and a limited range of insecticide options. Biological control presents a promising sustainable alternative. Our previous work suggested the La Jolla Virus (LJV) as a suitable candidate for the development of an insect virus-based control option. Here, we characterized the natural transmission and pathology of the virus. We tested various modes of horizontal transmission, including airborne, venereal and oral, and fecal routes. To understand LJV pathology in infected flies, we studied feeding behavior and demonstrated changes in food absorption compared to non-infected flies. We also investigated the impact on fecundity and egg-to-adult success rate. Altogether, these results collectively improve our understanding of LJV transmission in natural populations and the implication of infected flies in food ingestion and overall fitness.
Keywords: Drosophila suzukii; La Jolla virus; biological pest control; food intake; iflavirus; transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Optimizing irradiation dose for Drosophila melanogaster males to enhance heterospecific Sterile Insect Technique (h-SIT) against Drosophila suzukii.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 3;20(7):e0320546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320546. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40608745 Free PMC article.
-
Entomopathogenic Bacillus cereus impairs the fitness of the spotted-wing drosophila, Drosophila suzukii.Insect Sci. 2025 Jun;32(3):912-926. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.13439. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Insect Sci. 2025. PMID: 39169715
-
The Potential of Plant-Based Biorational Products for the Drosophila suzukii Control: Current Status, Opportunities, and Limitations.Neotrop Entomol. 2024 Apr;53(2):236-243. doi: 10.1007/s13744-023-01119-0. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Neotrop Entomol. 2024. PMID: 38133734
-
An insect virus differentially alters gene expression among life stages of an insect vector and enhances bacterial phytopathogen transmission.J Virol. 2025 Jan 31;99(1):e0163024. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01630-24. Epub 2024 Dec 23. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 39714167 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Deprá M., Poppe J.L., Schmitz H.J., De Toni D.C., Valente V.L.S. The first records of the invasive pest Drosophila suzukii in the South American continent. J. Pest Sci. 2014;87:379–383. doi: 10.1007/s10340-014-0591-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

