Colorimetric Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Xylenol Orange Targeting Nucleocapsid Gene for Detection of Feline Coronavirus Infection
- PMID: 40143345
- PMCID: PMC11946810
- DOI: 10.3390/v17030418
Colorimetric Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Xylenol Orange Targeting Nucleocapsid Gene for Detection of Feline Coronavirus Infection
Abstract
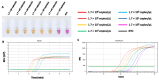
Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP), a devastating disease with near-complete mortality, is caused by the feline coronavirus (FCoV) and affects domestic cats worldwide. Herein, we report the development of a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) assay incorporating xylenol orange (XO) as a visual indicator for FCoV detection. The assay employed six oligonucleotide primers targeting regions of the nucleocapsid (N) gene. Under optimized conditions (65 °C, 60 min), amplification products were detected through pH-dependent colour changes in the XO dye. The RT-LAMP-XO assay exhibited high specificity for FCoV, with no cross-reactivity against other common feline viral pathogens. While the detection limit (1.7 × 101 copies/µL) was an order of magnitude higher than that of qPCR, the method offered advantages in simplicity and speed compared to existing diagnostic approaches. Although less sensitive than qPCR, the RT-LAMP-XO assay may serve as a rapid screening tool when used in combination with additional primer sets. These findings demonstrate the potential utility of XO-based RT-LAMP as a simple, visual detection method for FCoV infection.
Keywords: FIP; RT-LAMP; Xylenol orange; feline corona virus; qPCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Masters P.S., Perlman S. Coronaviridae. Fields Virol. 2013;1:825–858.
-
- Ehmann R., Kristen-Burmann C., Bank-Wolf B., König M., Herden C., Hain T., Thiel H.J., Ziebuhr J., Tekes G. Reverse Genetics for Type I Feline Coronavirus Field Isolate to Study the Molecular Pathogenesis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis. mBio. 2018;9:e01422-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01422-18. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

