Identification of biomarkers of shrinkage modes after neoadjuvant therapy in HER-2 positive breast cancer
- PMID: 40143733
- PMCID: PMC12165485
- DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002349
Identification of biomarkers of shrinkage modes after neoadjuvant therapy in HER-2 positive breast cancer
Abstract
Purpose: A nomogram to predict shrinkage modes after neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) was constructed in HER-2 positive (HER2+) breast cancer. The value and mechanism of targeting long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) as efficacy prediction biomarker was also evaluated.
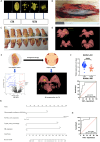
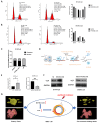
Methods: All enrolled patients received six cycles of chemotherapy (Docetaxel + Carboplatin) and anti-HER-2 dual-targeted therapy (Trastuzumab + Pertuzumab) before surgery. According to pathological three-dimensional (3D) models of residual tumor from 71 HER2+ patients, shrinkage modes were divided into concentric shrinkage mode (CSM) and non-CSM (NCSM). LncRNAs in core biopsy tissues in the CSM and NCSM groups were selected by microarray and validated by RT-PCR. A nomogram was constructed to predict shrinkage modes after NAT in combination with clinical-pathological and transcriptome signatures. Cell proliferation was used CCK-8 and colony formation assay. PAPIS Kit was used to perform nuclear and cytoplasmic separation. The cell drug resistance assays were to explore the value of paclitaxel. The ChIRP-MS assay was to search RNA-binding proteins and verified by WB. Cell cycle analysis was carried out by flow cytometry.
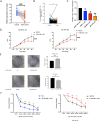
Results: Independent predictors of NCSM were lymph nodes downstaging after NAT, mammographic malignant calcification, hormone receptor expression, and RUVBL1-AS1 expression. A nomogram was constructed in combination with these predictors, which showed an area under the curve of 0.883, supporting the predictive power of the method. Overexpression of RUVBL1-AS1 inhibited HER2+ cells proliferation. Overexpression of RUVBL1-AS1 increased the number of cells in G1/S phase and decreased that of cells in G2 phase. RUVBL1-AS1 increased paclitaxel resistance and downregulated VCP expression. RUVBL1-AS1 affects cell cycle progression by downregulating VCP, resulting in the reduction of cells in G2/M phase, thereby weakening the sensitivity to paclitaxel.
Conclusion: The nomogram could accurately predict shrinkage modes after NAT, and may help guide the individualized selection of breast conserving surgery candidates after NAT. RUVBL1-AS1 might be a promising therapeutic target of paclitaxel-based chemotherapy inHER2+ breast cancer.
Keywords: RUVBL1-AS1; breast cancer; neoadjuvant therapy; nomogram; shrinkage modes.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have stated that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Houlahan KE, Khan A, Greenwald NF, et al. Germline-mediated immunoediting sculpts breast cancer subtypes and metastatic proclivity. Science 2024;384:eadh8697. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

