Antioxidants for the management of oral leukoplakia: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40144648
- PMCID: PMC11932839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2025.03.001
Antioxidants for the management of oral leukoplakia: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Introduction: Oral leukoplakia (OL) is a potentially malignant disorder characterized by non-scrabble white lesions that may turn into invasive carcinoma if left untreated. Few antioxidant treatments have shown promising results in the regression of lesions and prevention of their progression to carcinoma. We aim to summarize the current evidence on the effectiveness of antioxidants in the management of OL.
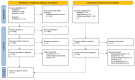
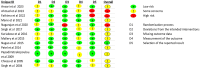
Materials and methods: The present systematic review followed PRISMA guidelines and involved a thorough search of three scientific databases: PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane. We used specific algorithms related to the keywords "antioxidant" and "Oral leukoplakia" to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that have explored the utility of antioxidants in the management of OL. The risk of bias assessment was conducted using the Cochrane risk of bias tool (ROB 2.0), ensuring the reliability of our findings.
Results: Out of 2490 articles retrieved, only thirteen RCTs involving 1147 participants fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Lycopene was found to be the most consistently effective antioxidant, showing significant effectiveness in reducing lesion size, both in oral and topical forms. The trials incorporating other antioxidants, including vitamin A, vitamin C, β-carotene, and curcumin, demonstrated mixed results. Severe heterogeneity was detected in treatment forms, dosage, administration frequency, treatment duration, and follow-up time among all included trials.
Conclusion: Lycopene may play a significant role in the non-surgical management of OL. Future research with large-scale, well-designed, randomized controlled trials with standardized dosing, delivery methods, and outcome measures is mandatory to provide more robust evidence on the available antioxidant therapy for OL.
Keywords: Antioxidant treatment; Leukoplakia; OPMD; Oral; Premalignant oral lesion.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources