Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Potential Predictive Marker for Epileptic Seizures: Unveiling the "V"-Shaped Link
- PMID: 40144751
- PMCID: PMC11944842
- DOI: 10.1155/mi/2247724
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Potential Predictive Marker for Epileptic Seizures: Unveiling the "V"-Shaped Link
Abstract
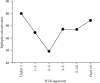
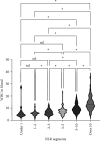
Objective: The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is an important marker of inflammation. An increased NLR has been detected in the blood of patients with epilepsy. However, the correlation between varying NLRs and epileptic seizures (ESs) is still unclear. Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted, and patients were divided into two groups based on whether they had ES upon admission. Comprehensive data were collected, including routine blood tests, demographic information, and medical histories. The NLR was calculated by dividing the percentage of neutrophils by the percentage of lymphocytes. Results: In total, 414 patients were included (284 males, 151 females; aged 18-90 years), with 271 in the experimental group and 143 in the control group. No significant differences in the NLR were found between the groups (p=0.164). Nonetheless, when NLRs were categorized, a "V"-shaped link with ES was observed. An NLR of 2-3 correlated with the lowest seizure incidence. Higher NLRs were associated with increased neutrophil and decreased lymphocyte counts. Patients with an NLR < 2 had the lowest infection rates and the highest cerebrovascular disease exposure, whereas those with an NLR > 3 had the highest infection rates and were the oldest. Conclusions: NLR modifications can serve as potential predictive markers for ES. However, the relationship between the NLR and ES is not linear. The factors contributing to these variations are multiple and complex. An NLR of 2-3 may represent an equilibrium point. An elevated NLR indicates pronounced inflammatory responses, while a low NLR can have more complex causes.
Keywords: epilepsy; inflammation; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; seizure.
Copyright © 2025 Xianmei Wang et al. Mediators of Inflammation published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Epilepsy. 2024. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy#:~:text=Rates%... .
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

