Role of the Wnt signaling pathway in the complex microenvironment of breast cancer and prospects for therapeutic potential (Review)
- PMID: 40145557
- PMCID: PMC12068849
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5742
Role of the Wnt signaling pathway in the complex microenvironment of breast cancer and prospects for therapeutic potential (Review)
Abstract
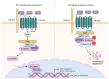
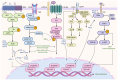
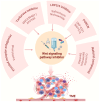
The focus on breast cancer treatment has shifted from the cytotoxic effects of single drugs on tumor cells to multidimensional multi‑pathway synergistic intervention strategies targeting the tumor microenvironment (TME). The activation of the Wnt signaling pathway in the TME of breast cancer cells serves a key regulatory role in tissue homeostasis and is a key driver of the carcinogenic process. Modulating the crosstalk between the Wnt pathway and TME of breast cancer is key for understanding the biological behavior of breast cancer and advancing the development of novel antitumor drugs. The present review aimed to summarize the complex mechanisms of the Wnt signaling pathway in the breast cancer TME, interactions between the Wnt signaling pathway and components of the breast cancer TME and breast cancer‑associated genes, as well as the interactions between the Wnt signaling pathway and other signaling cascades at the molecular level. Furthermore, the present review aimed to highlight the unique advantages of the Wnt signaling pathway in the macro‑regulation of the TME and the current therapeutic strategies targeting the Wnt signaling pathway, their potential clinical value and future research directions in breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: Wnt signaling pathway; breast cancer; pathway crosstalk; targeted therapy; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Wnt signaling in breast cancer: biological mechanisms, challenges and opportunities.Mol Cancer. 2020 Nov 24;19(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01276-5. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33234169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights about the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Primary Bone Tumors and Their Microenvironment: A Promising Target to Develop Therapeutic Strategies?Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 31;20(15):3751. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153751. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31370265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt signaling in the tumor microenvironment: A driver of brain tumor dynamics.Life Sci. 2024 Dec 1;358:123174. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123174. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39471897 Review.
-
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway as Chemotherapeutic Target in Breast Cancer: An Update on Pros and Cons.Clin Breast Cancer. 2020 Oct;20(5):361-370. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2020.04.004. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Clin Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32416986 Review.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in carcinogenesis and cancer therapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2024 Jun 18;17(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01563-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38886806 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim J, Harper A, McCormack V, Sung H, Houssami N, Morgan E, Mutebi M, Garvey G, Soerjomataram I, Fidler-Benaoudia MM. Global patterns and trends in breast cancer incidence and mortality across 185 countries. Nat Med. 2025 Feb 24; Epub ahead of print. - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez-Bejarano OH, Parra-López C, Patarroyo MA. A review concerning the breast cancer-related tumour microenvironment. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024;199:104389. - PubMed
-
- Park J, Hsueh PC, Li Z, Ho PC. Microenvironment-driven metabolic adaptations guiding CD8+ T cell anti-tumor immunity. Immunity. 2023;56:32–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

