A Comprehensive Review of Magnetic Nanocatalysts for C-S, C-Se Bond Formation
- PMID: 40145843
- PMCID: PMC12409848
- DOI: 10.1002/open.202500041
A Comprehensive Review of Magnetic Nanocatalysts for C-S, C-Se Bond Formation
Abstract
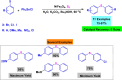
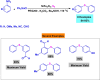
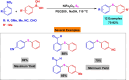
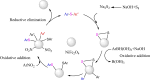
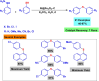
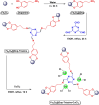
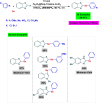
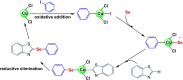
This review manuscript examines magnetic nanocatalysts and their pivotal role in forming carbon-sulfur (C-S) and carbon-selenium (C-Se) bonds. The study delves into the latest advancements in the synthesis, characterization, and application of magnetic nanocatalysts, highlighting their unique advantages, including enhanced catalytic activity, superior selectivity, and easy recovery through magnetic separation, which align with the principles of green chemistry. Through a critical analysis of recent research findings, this review also explores the mechanistic pathways facilitated by these nanocatalysts, offering insights into their operational efficiency and potential for recyclability. The manuscript aims not only to catalog the current achievements in this burgeoning field but also to identify challenges and propose future directions for developing more efficient, sustainable, and versatile catalytic systems for C-S and C-Se bond formation. By encompassing a broad spectrum of magnetic nanocatalysts, ranging from bare magnets to functionalized and composite materials, this review is a comprehensive resource for researchers engaged in organic synthesis, catalysis, and sustainable chemistry.
Keywords: C−S bond; C−Se bond; Synthesis; heterocycles; magnetic nanocatalysts.
© 2025 The Authors. ChemistryOpen published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
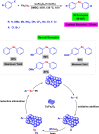


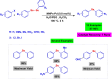
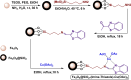
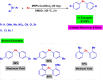


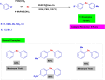
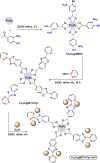
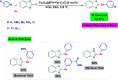
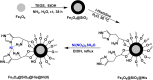
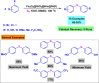
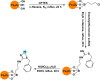
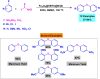
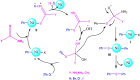









References
-
- Mondal S., Mukherjee P., Paul A., Sikdar A., Mandal B., ChemistrySelect 2023, 10, 10.1002/slct.202303212. - DOI
-
- Balati H., Zhi W., Ruan R., SynOpen 2023, 07, 511–520. 10.1055/a-2184-8411. - DOI
-
- Walsh C. T., ChemistrySelect 2023, 10, 136–171. 10.1039/bk9781839169502-00136. - DOI
-
- Min S. K., Xin J. Y., Zhenhua K., Green Synth. Catal. 2022, 3, 309–316. 10.1016/j.gresc.2022.09.002. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

