Treatment of nephrotic syndrome with anti-CD20 therapies in pregnancy: a case series and review of the literature
- PMID: 40148078
- PMCID: PMC11951322
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2481201
Treatment of nephrotic syndrome with anti-CD20 therapies in pregnancy: a case series and review of the literature
Abstract
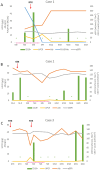
Membranous nephropathy (MN), focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) and minimal change disease (MCD) are autoimmune kidney diseases and the most common causes of nephrotic syndrome. Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies are now recommended as first-line therapy for MN. Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies are also effective in steroid-dependent or frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome associated with MCD or FSGS. Many women eligible for these treatments are of childbearing age. The impact of anti-CD20 therapies on pregnancy and fetal outcomes remains uncertain, particularly in glomerular diseases. We describe three cases of patients with glomerular disease treated with anti-CD20 therapies in the context of pregnancy and review the literature.
Keywords: Pregnancy; auto-immunity; nephrotic syndrome; obinutuzumab; rituximab.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
