Metformin prevents diabetes development in type 1 diabetes models via suppression of mTOR and STAT3 signaling in immune cells
- PMID: 40148472
- PMCID: PMC11950226
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-93647-5
Metformin prevents diabetes development in type 1 diabetes models via suppression of mTOR and STAT3 signaling in immune cells
Abstract
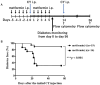
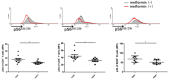
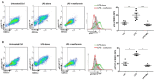
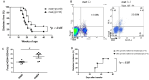
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an organ-specific autoimmune disease caused by T cell-mediated pancreatic β cell destruction. To evaluate the effects of metformin on immune cells in autoimmune diabetes, we administered metformin intraperitoneally to two T1D mouse models and analyzed autoimmune diabetes progression. In a cyclophosphamide (CY)-induced T1D model in male non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice, intraperitoneal administration of metformin significantly prevented autoimmune diabetes. Treatment with metformin showed a decrease in activated T cells, CD44hiCD62Llo effector memory cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells (DCs), and an increase in CD44hiCD62Lhi central memory cells, B cells, and regulatory T cells (Tregs) in splenocytes. Interestingly, metformin treatment showed a decrease in activated T cells, CD4+ effector memory T cells and Th1-type antigen-specific cells in PLN cells. IL-17 production was significantly suppressed in metformin-treated mice. TNF-α production from DCs in vitro was dose-dependently suppressed by metformin. Activity of mTOR signaling was significantly reduced in CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and B220+ B cells. In addition, activities of mTOR and STAT3 signaling in DCs were also reduced significantly. Furthermore, metformin treatment in female NOD mice, a spontaneous T1D model, significantly suppressed autoimmune diabetes onset as well and an increase in Tregs was observed. Our results suggest that metformin may suppress autoimmunity and have therapeutic potential in T1D progression as an immunomodulator.
Keywords: AMPK; Immunomodulator; Metformin; STAT3; Type 1 diabetes; mTOR.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




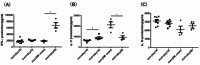

References
-
- Eisenbarth, G. S. Type I diabetes mellitus. A chronic autoimmune disease. N. Engl. J. Med.314, 1360–1368 (1986). - PubMed
-
- Makino, S. et al. Breeding of a non-obese, diabetic strain of mice. Jikken Dobutsu. 29, 1–13 (1980). - PubMed
-
- Dahlen, E., Dawe, K., Ohlsson, L. & Hedlund, G. Dendritic cells and macrophages are the first and major producers of TNF-alpha in pancreatic islets in the nonobese diabetic mouse. J. Immunol.160, 3585–3593 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Banchereau, J. & Steinman, R. M. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature392, 245–252 (1998). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

