The effect of hydroxychloroquine on activities of daily living and hand function in systemic sclerosis: results from an analysis of the EUSTAR cohort
- PMID: 40148996
- PMCID: PMC11948955
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-025-03476-0
The effect of hydroxychloroquine on activities of daily living and hand function in systemic sclerosis: results from an analysis of the EUSTAR cohort
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the use of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and its impact on the Health Assessment Questionnaire disability index(HAQ-DI) and the Cochin Hand Function Status(CHFS) in a large Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) cohort.
Methods: SSc patients from the European Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database treated with HCQ for at least 6 months were evaluated and compared to a matched group of SSc patients not using HCQ. Demographic and clinical data, concomitant drugs, HAQ-DI and CHFS (at least 2 evaluations) were recorded and were the outcome variables of interest. Statistical analysis was performed using propensity score matching for age, gender, disease duration, corticosteroids, immunosuppressives, vasoactive drugs in a 3:1 control: HCQ ratio. Standard descriptive statistics and Student's t-test and Chi-square test were used to assess the propensity-matched groups.
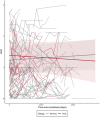
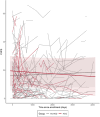
Results: Out of 17,805 SSc patients evaluated, 468 (2.6%) used HCQ and constituted the HCQ group. Among them, 50 (10.7%) had at least a baseline and follow-up HAQ-DI evaluation and 44 (9.4%) had at least a baseline and follow-up CHFS evaluation. Propensity matching assured that patients were matched for female gender (HCQ vs. control 92.0% vs. 85.3%), mean age (49.8 vs. 50.0 years) disease duration (8.3 vs. 9.1 years), limited disease (55.3 vs. 62.6%) as well as background medications (all P > 0.1). We did not find any significant differences among the two groups in the change of HAQ-DI or CHFS, over up to 365 days (all P > 0.05).
Conclusions: Results from the EUSTAR registry showed that HCQ was used by 2.6% of SSc patients. HCQ use did not improve the HAQ-DI, or CHFS when comparing HCQ users to non-HCQ users.
Keywords: Hand function; Hydroxychloroquine; Quality of life; Systemic sclerosis; Treatment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All contributing EUSTAR centres have obtained approval from their respective local ethics committee for including patients’ data in the EUSTAR database and written informed consent was obtained in those centres, where required by the ethics committee. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: Bruni C: speaker for Eli-Lilly, consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim. Research grants from Foundation for Research in Rheumatology (FOREUM), Gruppo Italiano Lotta alla Sclerodermia (GILS), European Scleroderma Trials and Research Group (EUSTAR), Foundation for research in Rheumatology (FOREUM), Scleroderma Clinical Trials Consortium (SCTC) and Scleroderma Research Foundation (SRF). Educational grants from AbbVie outside the submitted work. Distler O has/had consultancy relationship with and/or has received research funding from and/or has served as a speaker for the following companies in the area of potential treatments for systemic sclerosis and its complications in the last three calendar years: 4P-Pharma, Abbvie, Acceleron, Alcimed, Altavant, Amgen, AnaMar, Arxx, AstraZeneca, Blade, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Corbus, CSL Behring, Galderma, Galapagos, Glenmark, Gossamer, Horizon, Janssen, Kymera, Lupin, Medscape, Merck, Miltenyi Biotec, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Novartis, Prometheus, Redxpharma, Roivant and Topadur. Co-founder of Citus AG. Patent issued “mir-29 for the treatment of systemic sclerosis” (US8247389, EP2331143)outside the submitted work. Distler O has/had consultancy relationship with and/or has received research funding from and/or has served as a speaker for the following companies in the area of potential treatments for systemic sclerosis and its complications in the last three calendar years: 4P-Pharma, Abbvie, Acceleron, Alcimed, Altavant, Amgen, AnaMar, Arxx, AstraZeneca, Blade, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Corbus, CSL Behring, Galderma, Galapagos, Glenmark, Gossamer, Horizon, Janssen, Kymera, Lupin, Medscape, Merck, Miltenyi Biotec, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Novartis, Prometheus, Redxpharma, Roivant and Topadur. Co-founder of Citus AG. Patent issued “mir-29 for the treatment of systemic sclerosis” (US8247389, EP2331143) Outside the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Meier FM, Frommer KW, Dinser R, et al. Update on the profile of the EUSTAR cohort: an analysis of the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research group database. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:1355. - PubMed
-
- Varga J, Maria T, Masataka K. Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: recent insights of molecular and cellular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2017;2(3):137. 10.5301/jsrd.500024.
-
- Rannou F, Poiraudeau S, Berezné A, et al. Assessing disability and quality of life in systemic sclerosis: construct validities of the Cochin Hand Function Scale, Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), systemic sclerosis HAQ, and medical outcomes study 36-Item short. Form Health Surv Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57(1):94–102. - PubMed
-
- Fries JF, Spitz P, Kraines RG, Holman HR. Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1980;23:137–45. - PubMed
-
- Duruoz MT, Poiraudeau S, Fermanian J, et al. Development and validation of a rheumatoid hand functional disability scale that assesses functional handicap. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:1167–72. - PubMed