Antimicrobial Stewardship Impact on Antibiotic Use in Three Tertiary Hospitals in Zambia: A Comparative Point Prevalence Survey
- PMID: 40149095
- PMCID: PMC11939251
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics14030284
Antimicrobial Stewardship Impact on Antibiotic Use in Three Tertiary Hospitals in Zambia: A Comparative Point Prevalence Survey
Abstract
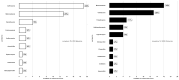
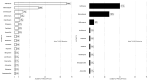
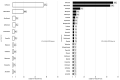
Introduction: Antimicrobial stewardship (AMS) can improve the rational use of antibiotics in hospitals. This study assessed the impact of a multifaceted AMS intervention on antibiotic use and prescribing patterns at three tertiary hospitals in Zambia. Methods: Point Prevalence Surveys (PPS) were conducted in three tertiary hospitals in August 2022 and in October 2023. It was part of a 3-year AMS demonstration project that aimed to optimize the use of antibiotics in treating urinary tract infections (UTIs) and bloodstream infections (BSIs) in various health sector settings in Zambia. Up to 170 medical records in 2022 and 265 in 2023 were included in the assessment. Results: Overall, the prevalence of antibiotic use in this PPS was 75%. Eighty-one percent (81%) and 71% of patients assessed were on at least one antibiotic in 2022 and 2023, respectively, indicating a decrease of 10%. Similarly, prescribing ceftriaxone, the most prescribed antibiotic, declined from an average of 48% in 2022 to 38% in 2023. Adherence to Standard Treatment Guidelines (STGs) slightly increased from 42% in 2022 to 45% in 2023. Additionally, antibiotic prescribing was reduced from 1.38 to 1.21. Conclusions: Antimicrobial stewardship had an early positive impact on antibiotic use and adherence to Standard Treatment Guidelines.
Keywords: Zambia; antimicrobial stewardship; impact; interventions; point prevalence survey.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

