The Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Target Claudin 6 Is a Marker for Early Organ-Specific Epithelial Progenitors and Is Expressed in Some Pediatric Solid Tumor Entities
- PMID: 40149257
- PMCID: PMC11940025
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17060920
The Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Target Claudin 6 Is a Marker for Early Organ-Specific Epithelial Progenitors and Is Expressed in Some Pediatric Solid Tumor Entities
Abstract
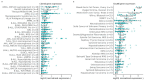
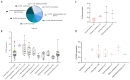
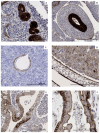
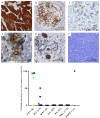
Background/Objectives: The oncofetal membrane protein Claudin 6 (CLDN6) is an attractive target for T cell-based therapies. There is a lack of detailed analyses on the age-dependent expression of CLDN6 in normal tissues is lacking, which limits the expansion of CLDN6 CAR-T cell clinical trials to pediatric populations. Methods: We analyzed CLDN6 expression in extracranial solid tumors and normal tissues of children using RNA-sequencing data from over 500 pediatric solid tumor samples, qRT-PCR and immunohistochemistry (IHC) in more than 100 fresh-frozen tumor samples and, approximately, 250 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples. We examined normal tissue expression via qRT-PCR in 32 different infant tissues and via IHC in roughly 290 tissues from donors across four age groups, as well as in fetal autopsy samples. Results: In fetal tissues, we detected CLDN6 expression primarily in the epithelial cells of several organs, including the skin, lungs, kidneys, intestinal tract, and pancreas, but not in undifferentiated blastemal cells. Postnatally, we found CLDN6-positive epithelial progenitors only during the first few weeks of life. In older-age groups, isolated clusters of CLDN6-positive progenitors were present, but in scarce quantities. In tumor tissues, we found strong and homogeneous CLDN6 expression in desmoplastic small round cell tumors and germ cell tumors. Wilms tumors demonstrated heterogeneous CLDN6 expression, notably absent in the blastemal component. Conclusions: These findings highlight an organ-specific presence of CLDN6-positive epithelial precursors that largely disappear in terminally differentiated epithelia within weeks after birth. Therefore, our data support CLDN6 as a viable therapeutic target in pediatric patients and justify their inclusion in basket studies for anti-CLDN6-based therapies.
Keywords: CAR-T cells; Claudin 6; Wilms tumors; desmoplastic small round cell tumors; germ cell tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
M.L.: Employment and stock ownership at BioNTech SE. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Erdmann F., Kaatsch P., Grabow D., Spix C. German Childhood Cancer Registry—Annual Report 2019 (1980–2018) Institute of Medical Biostatistics, Epidemiology and Informatics (IMBEI) at the University Medical Center of the Johannes Gutenberg University; Mainz, Germany: 2020.
-
- Ladenstein R., Potschger U., Valteau-Couanet D., Luksch R., Castel V., Yaniv I., Laureys G., Brock P., Michon J.M., Owens C., et al. Interleukin 2 with anti-GD2 antibody ch14.18/CHO (dinutuximab beta) in patients with high-risk neuroblastoma (HR-NBL1/SIOPEN): A multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2018;19:1617–1629. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30578-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maude S.L., Laetsch T.W., Buechner J., Rives S., Boyer M., Bittencourt H., Bader P., Verneris M.R., Stefanski H.E., Myers G.D., et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018;378:439–448. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1709866. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Minard-Colin V., Auperin A., Pillon M., Burke G.A.A., Barkauskas D.A., Wheatley K., Delgado R.F., Alexander S., Uyttebroeck A., Bollard C.M., et al. Rituximab for High-Risk, Mature B-Cell Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382:2207–2219. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1915315. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McLeod C., Gout A.M., Zhou X., Thrasher A., Rahbarinia D., Brady S.W., Macias M., Birch K., Finkelstein D., Sunny J., et al. St. Jude Cloud: A Pediatric Cancer Genomic Data-Sharing Ecosystem. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:1082–1099. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1230. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

