CDK4/6 as a Therapeutic Target in HR+/HER2- Breast Cancer Cells-Current Treatment Status
- PMID: 40149372
- PMCID: PMC11940879
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17061039
CDK4/6 as a Therapeutic Target in HR+/HER2- Breast Cancer Cells-Current Treatment Status
Abstract
Breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed neoplasm in the world. It can be classified into four main subtypes, each of them showing differences in the expression of hormone receptor (HR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and in cell metabolism. Since 2015, when The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor that regulates the cell cycle, treatment of HR+/HER2- BC has become much more effective. Currently, palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib are more often used both in combination with endocrine therapy as well as in monotherapy. Their application has been extensively verified in many clinical trials such as PALOMA-1,2,3, MONALEESA-1,2,3,7, and MONARCH-1,2,3, which allowed the verification of differences in their effectiveness, dosage, and adverse effects. Subsequent studies, MonarchE and NATALEE, examined the role of these inhibitors as adjuvant therapy, as well as at verifying their safety. Moreover, dalpiciclib is being investigated in HR+/HER2- BC treatment. This article will summarize clinical efficacy, recommendations, and differences in toxicity profile between palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib and will also discuss the possibility of using dalpiciclib in the treatment of breast cancer.
Keywords: CDK4/6 inhibitors; HR+/HER2−; abemaciclib; breast cancer; dalpiciclib; palbociclib; ribociclib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
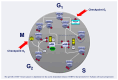
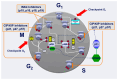
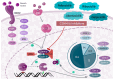
References
-
- Female Breast Cancer—Cancer Stat Facts. [(accessed on 14 December 2024)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

