Cryptic KMT2A::AFDN Fusion Due to AFDN Insertion into KMT2A in a Patient with Acute Monoblastic Leukemia
- PMID: 40149468
- PMCID: PMC11942050
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16030317
Cryptic KMT2A::AFDN Fusion Due to AFDN Insertion into KMT2A in a Patient with Acute Monoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
Background: KMT2A rearrangements occur in ~10% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cases and are critical for classification, risk stratification, and use of targeted therapy. However, insertions involving the KMT2A gene can evade detection using chromosomal analysis and/or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).
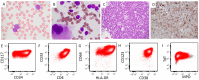
Methods: We present a case of a 22-year-old woman with acute monoblastic leukemia harboring a cryptic KMT2A::AFDN fusion identified by RNA sequencing. Initial FISH showed a 3' KMT2A deletion, while conventional karyotyping and the automated bioinformatic pipeline for optical genome mapping (OGM) did not identify the canonical translocation.
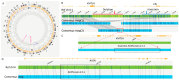
Results: To resolve these discrepancies, metaphase KMT2A FISH (break-apart fusion probe) was performed to assess whether KMT2A was translocated to another chromosome. However, the results did not support this possibility. As the fusion signal remained on the normal chromosome 11, with the 5' KMT2A signal localized to the derivative chromosome 11. A subsequent manual review of the OGM data revealed a cryptic ~300 kb insertion of AFDN into the 3' region of KMT2A, reconciling the discrepancies between chromosomal analysis, FISH, and RNA fusion results.
Conclusions: This case highlights the importance of integrating multiple testing modalities with expert review when there is a discrepancy. Our findings emphasize the need for a comprehensive approach to genomic assessment to enhance diagnostic accuracy and guide therapeutic decision-making.
Keywords: KMT2A::AFDN rearrangement; RNA fusion panel; acute monocytic leukemia; fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH); optical genome mapping.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mrózek K., Heinonen K., Lawrence D., Carroll A.J., Koduru P.R., Rao K.W., Strout M.P., Hutchison R.E., Moore J.O., Mayer R.J., et al. Adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia and t(9; 11)(p22; q23) have a superior outcome to patients with other translocations involving band 11q23: A cancer and leukemia group B study. Blood. 1997;90:4532–4538. doi: 10.1182/blood.V90.11.4532. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Balgobind B.V., Raimondi S.C., Harbott J., Zimmermann M., Alonzo T.A., Auvrignon A., Beverloo H.B., Chang M., Creutzig U., Dworzak M.N., et al. Novel prognostic subgroups in childhood 11q23/MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia: Results of an international retrospective study. Blood. 2009;114:2489–2496. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-04-215152. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

