Relationship Between Vitamin D Receptor Gene BsmI Polymorphism and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Total Levels in Slovak Postmenopausal Women with Reduced Bone Mineral Density
- PMID: 40149488
- PMCID: PMC11941902
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16030337
Relationship Between Vitamin D Receptor Gene BsmI Polymorphism and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Total Levels in Slovak Postmenopausal Women with Reduced Bone Mineral Density
Abstract
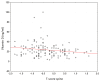
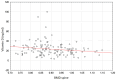
Objectives: The BsmI polymorphism of the VDR gene (vitamin D receptor) is one of the important genetic variants influencing the development of osteoporosis. Measurement and evaluation of the 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) concentration in individuals with reduced bone mineral density are essential because deficiency of this hormone causes impaired bone mineralization, leads to low BMD (bone mineral density), and influences fracture formation. The aim of the study was to investigate the relationship between the VDR gene BsmI polymorphism and 25(OH)D levels in Slovak postmenopausal women. Materials and Methods: The study population consisted of 287 untreated postmenopausal women, who were divided into three groups based on T-scores: normal (CG = 65), osteopenia (OPE = 126), and osteoporosis (OPO = 96). DNA isolation was performed using a standard protocol. Genetic analyses of the BsmI (rs1544410) polymorphism of the VDR gene were performed using the TaqMan SNP genotyping assays. Biochemical analysis of total 25(OH)D was performed in blood serum using the electrochemiluminescence method. Results: The chi-square test confirmed that the mutant T allele was not associated with the development of osteoporosis (p = 0.419). Through Kruskal-Wallis analysis, we found significant differences (p < 0.05, p < 0.01) in total 25(OH)D concentrations in individual genotypes of the BsmI variant of the VDR gene between the groups of women studied. Conclusions: It can be concluded that the VDR gene and its variant BsmI as well as 25(OH)D total may be relevant markers in the etiology of the search for individuals at risk of osteoporosis.
Keywords: 25(OH)D total; VDR gene; biomarkers; bone mineral density; gene variant BsmI.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vitamin D Status, Bone Mineral Density, and VDR Gene Polymorphism in a Cohort of Belarusian Postmenopausal Women.Nutrients. 2021 Mar 4;13(3):837. doi: 10.3390/nu13030837. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33806559 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) polymorphism with osteoporotic changes in Polish postmenopausal women.Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2009;30(4):540-6. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2009. PMID: 20010502
-
Vitamin D status and the Cdx-2 polymorphism of the vitamin D receptor gene are determining factors of bone mineral density in young healthy postmenopausal women.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Jul;136:187-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.09.026. Epub 2012 Sep 28. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23026509 Review.
-
Polymorphisms in VDR gene in Tunisian postmenopausal women are associated with osteopenia phenotype.Climacteric. 2015;18(4):624-30. doi: 10.3109/13697137.2015.1007123. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Climacteric. 2015. PMID: 25603555
-
Association Between Vitamin D Receptor BsmI Polymorphism and Low Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women in the MENA Region.Pathophysiology. 2025 Feb 1;32(1):6. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology32010006. Pathophysiology. 2025. PMID: 39982362 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of vitamins in the development and treatment of osteoporosis (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Jul;56(1):109. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5550. Epub 2025 May 16. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40376992 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khammissa R.A.G., Fourie J., Motswaledi M.H., Ballyram R., Lemmer J., Feller L. The Biological Activities of Vitamin D and Its Receptor in Relation to Calcium and Bone Homeostasis, Cancer, Immune and Cardiovascular Systems, Skin Biology, and Oral Health. BioMed Res. Int. 2018;2018:9276380. doi: 10.1155/2018/9276380. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen X., Shen L., Gao C., Weng R., Fan Y., Xu S., Zhang Z., Hu W. Vitamin D status and its associations with bone mineral density, bone turnover markers, and parathyroid hormone in Chinese postmenopausal women with osteopenia and osteoporosis. Front. Nutr. 2024;10:1307896. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1307896. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical