Fabry Disease: Insights into Pathophysiology and Novel Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 40149601
- PMCID: PMC11940501
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13030624
Fabry Disease: Insights into Pathophysiology and Novel Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
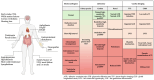
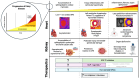
Fabry disease (FD) is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder characterized by deficiency of α-galactosidase A (α-GalA), leading to the accumulation of glycosphingolipids and multi-organ dysfunction, particularly affecting the cardiovascular and renal systems. Disease-modifying treatments such as enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) and oral chaperone therapy (OCT) have limited efficacy, particularly in advanced disease, prompting a need for innovative therapeutic approaches targeting underlying molecular mechanisms beyond glycosphingolipid storage alone. Recent insights into the pathophysiology of FD highlights chronic inflammation and mitochondrial, lysosomal, and endothelial dysfunction as key mediators of disease progression. Adjunctive therapies such as sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) demonstrate significant cardiovascular and renal benefits in conditions including heart failure and chronic kidney disease. These drugs also modulate pathways involved in the pathophysiology of FD, such as autophagy, oxidative stress, and pro-inflammatory cytokine signaling. While theoretical foundations support their utility, dedicated trials are necessary to confirm efficacy in the FD-specific population. This narrative review highlights the importance of expanding therapeutic strategies in FD, advocating for a multi-faceted approach involving evidence-based adjunctive treatments to improve outcomes. Tailored research focusing on diverse FD phenotypes, including females and non-classical variants of disease, will be critical to advancing care and improving outcomes in this complex disorder.
Keywords: Fabry disease; chronic kidney disease; heart failure; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Biegstraaten M., Arngrímsson R., Barbey F., Boks L., Cecchi F., Deegan P.B., Feldt-Rasmussen U., Geberhiwot T., Germain D.P., Hendriksz C., et al. Recommendations for initiation and cessation of enzyme replacement therapy in patients with Fabry disease: The European Fabry Working Group consensus document. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015;10:36. doi: 10.1186/s13023-015-0253-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

