Impact of Protein Kinase C Activation and Monoclonal Antibodies on Immune Checkpoint Regulation and B Cell Function in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
- PMID: 40149717
- PMCID: PMC11940456
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13030741
Impact of Protein Kinase C Activation and Monoclonal Antibodies on Immune Checkpoint Regulation and B Cell Function in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
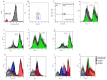
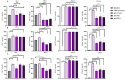
Background: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is characterized by the proliferation of dysfunctional B cells, resulting in significant immune dysregulation. Patients with CLL exhibit varied responses to B cell receptor (BCR) targeted therapies, emphasizing the need for tailored immunotherapy approaches. This study investigated B cell function in untreated patients with CLL, and we further explored the effects of ex vivo protein kinase C activation on immune checkpoint expression and B cell profiles. Methods: Peripheral blood samples were collected from 21 untreated patients with CLL at King Edward Hospital in South Africa, between 2019 and 2022. B cells were stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) and ionomycin. Using flow cytometry, the study explored the levels of B cell subsets and immune checkpoint proteins programmed cell death 1 (PD-1), programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), programmed cell death-ligand 2 (PD-L2) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) expression on various B cell subsets. Results: PMA and ionomycin B cell stimulation upregulated PD-1, CTLA-4 and PD-L2 expression on B cell subsets (p < 0.01). As expected, monoclonal antibodies targeting PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4 significantly downregulated the CTLA-4 expression of B cell subsets (p < 0.05), while PD-L2 exhibited varied responses in different B cell subsets. Moreover, PD-1 and PD-L1 expression on total B cells significantly declined following their blockage (p < 0.01). In addition, these monoclonal antibodies increased the levels of CD19+CD27+ B cells (p < 0.0128) and activated CD19+CD27+ B cells (p < 0.01). Conclusions: Protein kinase C activation on B cells stimulates immune checkpoint expression. The use of monoclonal antibodies on B cells plays a critical role in the B cell function through the reduction in CD38 expressing activated B cells and upregulation of CD19+CD27+ B cells. Moreover, the monoclonal antibody targeting PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4 are effective in reducing the expression of CTLA-4 on B cell subsets, while PD-1 and PD-L1 blockage may be effective in reducing the expression of these immune checkpoints on total B cells.
Keywords: B cell subsets; chronic lymphocytic leukemia; immune checkpoint inhibitor; ionomycin; phorbol myristate acetate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
B Cell Subsets and Immune Checkpoint Expression in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Feb 23;46(3):1731-1740. doi: 10.3390/cimb46030112. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38534728 Free PMC article.
-
Control of PD-L1 expression in CLL-cells by stromal triggering of the Notch-c-Myc-EZH2 oncogenic signaling axis.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Apr;9(4):e001889. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001889. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33931470 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of PD-1 and TIM-3 immune checkpoints fails to restore the function of exhausted CD8+ T cells in early clinical stages of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Immunol Res. 2020 Oct;68(5):269-279. doi: 10.1007/s12026-020-09146-4. Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 32710227
-
The Next Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in Melanoma.Clin Ther. 2015 Apr 1;37(4):764-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 25823918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers for checkpoint inhibition in hematologic malignancies.Semin Cancer Biol. 2018 Oct;52(Pt 2):198-206. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2018.05.005. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018. PMID: 29775689 Review.
References
-
- Hallek M., Cheson B.D., Catovsky D., Caligaris-Cappio F., Dighiero G., Döhner H., Hillmen P., Keating M., Montserrat E., Chiorazzi N. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2018;131:2745–2760. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-09-806398. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

