Dia-B-Ties: B Cells in the Islet-Immune-Cell Interface in T1D
- PMID: 40149868
- PMCID: PMC11940010
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15030332
Dia-B-Ties: B Cells in the Islet-Immune-Cell Interface in T1D
Abstract
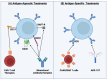
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease that affects an estimated 30 million people worldwide and results in a lifelong dependency of exogenous insulin treatments. While T1D is characterized by T-cell driven-destruction of the insulin-secreting β cells, B lymphocytes play a key role in the islet-immune interface. B cells are an essential intermediary between islet cells and other immune-cell populations. Through antigen presentation, cytokine secretion, and antibody production, B cells play a role in activating autoreactive islet-specific T cells, thus potentiating pancreatic inflammation in the early stages of T1D. Despite this, their role in disease development remains an understudied feature of T1D with significant therapeutic potential. Herein, we will discuss the current knowledge of the islet-immune-cell interface within T1D through the lens of B lymphocytes. We will also consider knowledge gaps that may be limiting further therapeutic opportunities.
Keywords: B cells; B lymphocytes; antigen-presenting cells; autoantibodies; insulitis; type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The extra-islet pancreas supports autoimmunity in human type 1 diabetes.Elife. 2025 Apr 15;13:RP100535. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100535. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40232951 Free PMC article.
-
Means, Motive, and Opportunity: Do Non-Islet-Reactive Infiltrating T Cells Contribute to Autoimmunity in Type 1 Diabetes?Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 16;12:683091. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.683091. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34220832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased inflammation as well as decreased endoplasmic reticulum stress and translation differentiate pancreatic islets from donors with pre-symptomatic stage 1 type 1 diabetes and non-diabetic donors.Diabetologia. 2025 Jul;68(7):1463-1475. doi: 10.1007/s00125-025-06417-3. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Diabetologia. 2025. PMID: 40457096 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of tyrosine protein-kinase 2 reduces islet inflammation and delays type 1 diabetes onset in mice.EBioMedicine. 2025 Jul;117:105734. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105734. Epub 2025 May 6. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40335415 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of hypoxia, immune dysregulation, and metabolic stress in pathophysiology of type 1 diabetes.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 4;16:1599321. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1599321. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40534855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akashi T., Nagafuchi S., Anzai K., Kondo S., Kitamura D., Wakana S., Ono J., Kikuchi M., Niho Y., Watanabe T. Direct evidence for the contribution of B cells to the progression of insulitis and the development of diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice. Int. Immunol. 1997;9:1159–1164. doi: 10.1093/intimm/9.8.1159. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

