Nanomaterial-Based Molecular Imaging in Cancer: Advances in Simulation and AI Integration
- PMID: 40149980
- PMCID: PMC11940464
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15030444
Nanomaterial-Based Molecular Imaging in Cancer: Advances in Simulation and AI Integration
Abstract
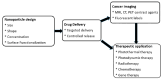
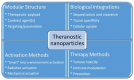
Nanomaterials represent an innovation in cancer imaging by offering enhanced contrast, improved targeting capabilities, and multifunctional imaging modalities. Recent advancements in material engineering have enabled the development of nanoparticles tailored for various imaging techniques, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), and ultrasound (US). These nanoscale agents improve sensitivity and specificity, enabling early cancer detection and precise tumor characterization. Monte Carlo (MC) simulations play a pivotal role in optimizing nanomaterial-based imaging by modeling their interactions with biological tissues, predicting contrast enhancement, and refining dosimetry for radiation-based imaging techniques. These computational methods provide valuable insights into nanoparticle behavior, aiding in the design of more effective imaging agents. Moreover, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) approaches are transforming cancer imaging by enhancing image reconstruction, automating segmentation, and improving diagnostic accuracy. AI-driven models can also optimize MC-based simulations by accelerating data analysis and refining nanoparticle design through predictive modeling. This review explores the latest advancements in nanomaterial-based cancer imaging, highlighting the synergy between nanotechnology, MC simulations, and AI-driven innovations. By integrating these interdisciplinary approaches, future cancer imaging technologies can achieve unprecedented precision, paving the way for more effective diagnostics and personalized treatment strategies.
Keywords: CT; MRI; Monte Carlo simulation; PAI; PET; US; artificial intelligence; cancer therapy; machine learning; medical imaging; nanomaterials; nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Monte Carlo Simulations in Nanomedicine: Advancing Cancer Imaging and Therapy.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Jan 15;15(2):117. doi: 10.3390/nano15020117. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39852732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in synthetic CT generation from MRI: A review of techniques, and trends in radiation therapy planning.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Nov;25(11):e14499. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14499. Epub 2024 Sep 26. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 39325781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in the diagnosis of biliopancreatic diseases: A comparative review and study on future insights.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2025 Apr 16;17(4):103391. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i4.103391. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2025. PMID: 40291132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI-Driven Advances in Low-Dose Imaging and Enhancement-A Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 11;15(6):689. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15060689. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating artificial intelligence with endoscopic ultrasound in the early detection of bilio-pancreatic lesions: Current advances and future prospects.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2025 Feb;74:101975. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2025.101975. Epub 2025 Jan 4. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40210329 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of nanomedicine and artificial intelligence in cancer health care: individual applications and emerging integrations-a narrative review.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 8;16(1):697. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02469-4. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40338421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in multimodal imaging techniques in nanomedicine: enhancing drug delivery precision.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 30;15(33):27187-27209. doi: 10.1039/d5ra03255e. eCollection 2025 Jul 25. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40740223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoradiopharmaceuticals: Design Principles, Radiolabeling Strategies, and Biomedicine Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 14;17(7):912. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070912. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing the potential of nanoparticles for cancer detection and precision therapeutics.Med Oncol. 2025 Jun 4;42(7):239. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02782-6. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40467942 Review.
-
Photoacoustic-Integrated Multimodal Approach for Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025 Jul 14;11(7):4033-4049. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5c00918. Epub 2025 Jul 1. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025. PMID: 40592765 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

