Contemporary Diagnosis, Management, and Early Outcomes in Children with Kawasaki Disease in Romania: A Single-Center Experience
- PMID: 40149999
- PMCID: PMC11940999
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15060656
Contemporary Diagnosis, Management, and Early Outcomes in Children with Kawasaki Disease in Romania: A Single-Center Experience
Abstract
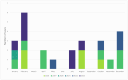
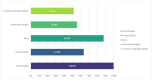
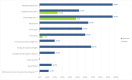
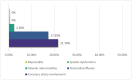
Background: Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute inflammatory vasculitis with a particularly high incidence of coronary artery complications and constitutes a significant cause of acquired heart disease in children and young adults. Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of consecutive patients aged 0-18 years hospitalized at the "Prof. Dr. Matei Balş" National Institute of Infectious Diseases in Bucharest with Kawasaki disease over a period of 6 years (2018-2023). Results: A total of 25 children were discharged from hospital with this diagnosis during the analyzed period. The mean age was 2.9 years, and 56% were boys. Fever ≥5 days was present in all cases, and the most frequent additional sign was the presence of oral changes. Patients were treated according to in-effect guidelines with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) (100%) and acetylsalicylic acid (68%). Only two cases were considered IVIG resistant and received a second IVIG infusion. Only mild cardiovascular changes were noted in echocardiography: mild coronary artery dilatation (21.7% of cases), mild valvular regurgitation, and small pericardial effusion. Infants displayed less inflammation and higher percentages of leukocytosis, developed an increase in platelet count sooner, received IVIG faster, and had longer hospital stays. Outcomes were generally favorable, and 92% of children were discharged, while the two remaining patients were transferred to other centers. No deaths were recorded. Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the largest contemporary Romanian cohort of Kawasaki disease published to date, outlining the local diagnostic process, therapeutic strategies, and early outcomes of Kawasaki disease.
Keywords: IVIG; Kawasaki; Romania; aspirin; coronary artery lesions; echocardiography; prolonged fever.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of intravenous immunoglobulin plus prednisolone therapy in patients with Kawasaki disease (Post RAISE): a multicentre, prospective cohort study.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018 Dec;2(12):855-862. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(18)30293-1. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018. PMID: 30337183
-
Kawasaki disease in Sicily: clinical description and markers of disease severity.Ital J Pediatr. 2016 Nov 2;42(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13052-016-0306-z. Ital J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27806720 Free PMC article.
-
Infliximab versus second intravenous immunoglobulin for treatment of resistant Kawasaki disease in the USA (KIDCARE): a randomised, multicentre comparative effectiveness trial.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021 Dec;5(12):852-861. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00270-4. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021. PMID: 34715057 Clinical Trial.
-
Kawasaki disease: a comprehensive review of treatment options.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2015 Dec;40(6):620-5. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12334. Epub 2015 Nov 7. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2015. PMID: 26547265 Review.
-
Kawasaki disease with shock as the primary manifestation: How to distinguish from toxic shock syndrome?: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Aug 2;103(31):e39199. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039199. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39093792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McCrindle B.W., Rowley A.H., Newburger J.W., Burns J.C., Bolger A.F., Gewitz M., Baker A.L., Jackson M.A., Takahashi M., Shah P.B., et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: A scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;135:e927–e999. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000484. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Son M.B.F. Kawasaki Disease: Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, and Etiology. [(accessed on 5 November 2024)]. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/kawasaki-disease-pathogenesis-epidemio....
-
- Doros G., Stroescu R., Olariu C., Ardelean A.M., Gafencu M. Cardiovascular involvement of Kawasaki disease in the west part of Romania. Jurnalul Pediatrului. 2017;20:18–23.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

