Simplatab: An Automated Machine Learning Framework for Radiomics-Based Bi-Parametric MRI Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 40150706
- PMCID: PMC11939345
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering12030242
Simplatab: An Automated Machine Learning Framework for Radiomics-Based Bi-Parametric MRI Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Background: Prostate cancer (PCa) diagnosis using MRI is often challenged by lesion variability.
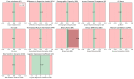
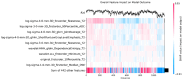
Methods: This study introduces Simplatab, an open-source automated machine learning (AutoML) framework designed for, but not limited to, automating the entire machine Learning pipeline to facilitate the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa) using radiomics features. Unlike existing AutoML tools such as Auto-WEKA, Auto-Sklearn, ML-Plan, ATM, Google AutoML, and TPOT, Simplatab offers a comprehensive, user-friendly framework that integrates data bias detection, feature selection, model training with hyperparameter optimization, explainable AI (XAI) analysis, and post-training model vulnerabilities detection. Simplatab requires no coding expertise, provides detailed performance reports, and includes robust data bias detection, making it particularly suitable for clinical applications.
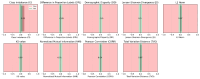
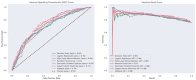
Results: Evaluated on a large pan-European cohort of 4816 patients from 12 clinical centers, Simplatab supports multiple machine learning algorithms. The most notable features that differentiate Simplatab include ease of use, a user interface accessible to those with no coding experience, comprehensive reporting, XAI integration, and thorough bias assessment, all provided in a human-understandable format.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that Simplatab can significantly enhance the usability, accountability, and explainability of machine learning in clinical settings, thereby increasing trust and accessibility for AI non-experts.
Keywords: AutoML; MRI; artificial intelligence; automated machine learning framework; open source; prostate cancer; radiomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Hietikko R., Kilpeläinen T.P., Kenttämies A., Ronkainen J., Ijäs K., Lind K., Marjasuo S., Oksala J., Oksanen O., Saarinen T., et al. Expected impact of MRI-related interreader variability on ProScreen prostate cancer screening trial: A pre-trial validation study. Cancer Imaging. 2020;20:72. doi: 10.1186/s40644-020-00351-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

