Electroacupuncture stimulation of auricular concha region improves loss of control over stress induced depression-like behavior by modulating 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor
- PMID: 40151119
- PMCID: PMC11955753
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.014
Electroacupuncture stimulation of auricular concha region improves loss of control over stress induced depression-like behavior by modulating 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor
Abstract
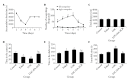
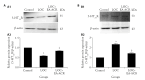
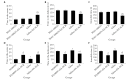
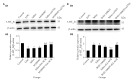
Objective: To observe whether electroacupuncture stimulation of auricular concha region (EA-ACR) on behavior changes of depression by loss of control over stress model (LOC), and whether its effect is improved by regulating the expression levels of hydroxytryptamine (serotonin, 5-HT) 1A receptor (5-HT1AR)/ hydroxytryptamine (serotonin, 5-HT) 2A receptor (5-HT2AR) in hippocampus.
Methods: LOC was prepared using a Skinner box, and EA-ACR to observe behavioral changes, and Western Blot was used to detect the changes of 5-HT1AR/5-HT2AR in the hippocampus, and then observe the changes of EA-ACR behavior after microinjection of 5-HT1AR/5-HT2AR antagonist into the hippocampus.
Results: EA-ACR improve depressive-like behavior, up-regulated 5-HT1AR expression and down-regulated 5-HT2AR expression in hippocampal brain area. EA-ACR did not improve depression-like behavior after hippocampal microinjection of 5-HT1AR antagonist, while injection of 5-HT2AR antagonists can improve depression-like behaviors.
Conclusion: EA-ACR can improve depressive-like behaviors. Loss of control over stress leads to up-regulation of 5-HT1AR and down-regulation of 5-HT2AR in the hippocampus, while EA-ACR mainly improves depressive behavior by regulating 5-HT1AR in Hip.
Keywords: auricular concha region; electroacupuncture stimulation; hippocampus; loss of control over stress; receptors, serotonin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture regulate hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and enhance hippocampal serotonin system in a rat model of depression.Neurosci Lett. 2016 Feb 26;615:66-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.01.004. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 26773866
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture stimulation of auricular concha region at different time-points on behavior changes in depression rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2012 Apr;37(2):131-5. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2012. PMID: 22764599 Chinese.
-
Electroacupuncture improves synaptic plasticity by regulating the 5-HT1A receptor in hippocampus of rats with chronic unpredictable mild stress.J Int Med Res. 2020 May;48(5):300060520918419. doi: 10.1177/0300060520918419. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32363965 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Central Serotonin Neurons and 5-HT Heteroreceptor Complexes in the Pathophysiology of Depression: A Historical Perspective and Future Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 15;22(4):1927. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041927. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33672070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin and brain function: a tale of two receptors.J Psychopharmacol. 2017 Sep;31(9):1091-1120. doi: 10.1177/0269881117725915. Epub 2017 Aug 31. J Psychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28858536 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022JQ-949/Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province: Acupuncture's Anxiolytic Effects in Uncontrollable Stress: Modulation of the Median Raphe Nucleus to Ventral Hippocampus Serotonergic Pathway
- 82004489/National Natural Science Foundation of China: Study on the Mechanisms of Learning and Memory Impairment induced by Chronic Pain and the Intervention Effects of Acupuncture
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
