Efficacy and safety of Qingwei Zhitong pellets-containing quadruple therapy for eradication: a prospective, single-center, randomized trial
- PMID: 40151129
- PMCID: PMC11955757
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.021
Efficacy and safety of Qingwei Zhitong pellets-containing quadruple therapy for eradication: a prospective, single-center, randomized trial
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of 14-day Qingwei Zhitong pellets (, QZ)-containing quadruple therapy (QZQT) compared to bismuth-containing quadruple therapy (BQT) in treatment-naive patients with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection.
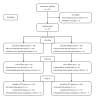
Methods: This single-center, randomized controlled clinical trial enrolled 333 patients, who were divided into either the QZQT group (QZ pellets, 3.2 g, three times daily; rabeprazole, 10 mg, twice daily; amoxicillin 1000 mg, twice daily; clarithromycin, 500 mg, twice daily) or the BQT group (bismuth potassium citrate, 1000 mg, three times daily; rabeprazole, 10 mg, twice daily; amoxicillin, 1000 mg, twice daily; clarithromycin, 500 mg, twice daily) for 14 d. The 13C-urea breath test assessed eradication success at least four weeks after treatment. The primary outcome focused on the eradication rate, with secondary outcomes including safety and patient compliance.
Results: From August 2022 to June 2023, 342 subjects were screened, and 333 were randomized. The QZQT and BQT groups showed eradication rates of 68.9% and 67.8% (P = 0.838) by intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis, respectively, and 71.1% and 68.3% (P = 0.612) by per-protocol (PP) analysis, respectively. QZQT was non-inferior to BQT in both ITT and PP analyses. QZQT was associated with fewer side effects (57.8% of patients) than BQT (90.4%) (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The 14 d QZQT treatment demonstrates equal efficacy in eradicating H. pylori infection and improved patient compliance and safety compared to BQT. These results provide evidence supporting 14-day QZQT as an acceptable treatment for H. pyloriinfection.
Keywords: Qingwei Zhitong pellets; bismuth; eradication; quadruple therapy; randomized controlled trial.
Figures
References
-
- Ye H, Shi ZM, Chen Y, et al.. Innovative perspectives of integrated Chinese medicine on H. pylori. Chin J Integr Med 2018; 24: 873-80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous