Effect of Ferrule Height on the Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Teeth Restored With Glass Fiber Posts: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 40151713
- PMCID: PMC11946697
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.79583
Effect of Ferrule Height on the Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Teeth Restored With Glass Fiber Posts: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
Introduction: Restoration of endodontically treated teeth (ETT) presents a significant challenge due to compromised structural integrity. The ferrule effect is crucial in reinforcing teeth and improving fracture resistance. This study aimed to compare and evaluate the effect of different crown ferrules on the fracture resistance of ETT restored with a glass fiber post and to evaluate the failure pattern.
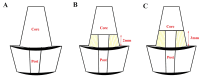
Materials and methods: Fifty-six extracted human maxillary central incisors were selected and randomly divided into four groups (n = 14 per group) based on ferrule height: Group 1 (control, no ferrule with a metal post), Group 2 (0 mm ferrule with a glass fiber post), Group 3 (2 mm ferrule with a glass fiber post), and Group 4 (3 mm ferrule with a glass fiber post). After endodontic treatment and post-space preparation, the teeth were restored using composite cores and full metal crowns. A universal testing machine was used to apply a compressive load at a 45° angle until fracture occurred. The fracture resistance was recorded in Newtons (N), and the failure modes were analyzed under a stereomicroscope. Statistical analysis was performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post-hoc Tukey test (p < 0.05).
Results: The mean fracture resistance values were highest in Group 1 (559.68 ± 92.52 N) and lowest in Group 2 (215.60 ± 70.79 N). Group 3 (428.53 ± 154.27 N) and Group 4 (439.06 ± 118.83 N) exhibited significantly higher fracture resistance than Group 2 (p = 0.001) but were not significantly different from each other (p = 0.950). Unfavorable root fractures were predominant in Group 1 and Group 2, whereas Group 3 and Group 4 showed repairable core-debonding failures.
Conclusions: Ferrules play a significant role in the fracture resistance of glass fiber post-restored teeth. Increasing the ferrule length significantly increases fracture resistance. Although metal posts provide higher fracture resistance, they are associated with a greater incidence of non-repairable failures. Glass fiber posts combined with an adequate ferrule are a more favorable option for restoring structurally compromised teeth.
Keywords: endodontically treated teeth; fracture; glass fiber; post; resistance.
Copyright © 2025, Rathaur et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
