Soman induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis of cerebral organoids via the GRP78-ATF6-CHOP signaling pathway
- PMID: 40152446
- PMCID: PMC12226415
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.70027
Soman induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis of cerebral organoids via the GRP78-ATF6-CHOP signaling pathway
Abstract
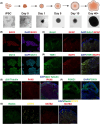
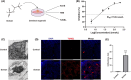
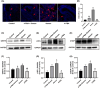
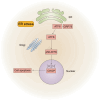
Soman is an organophosphorus compound that induces neurotoxicity. In addition to its direct toxic effects resulting from acetylcholine accumulation, neurotoxicity may also be exacerbated by inducing endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. In light of the current scarcity of appropriate in vitro assessment models, in the present study, we used cerebral organoids derived from human pluripotent stem cells, a new tool for investigating the mechanisms of neurotoxicity, to investigate soman-induced ER stress. The results demonstrated that soman significantly suppressed acetylcholinesterase activity and activated the GRP78-ATF6-CHOP (i.e. glucose-regulated protein 78-activating transcription factor 6-C/EBP homologous protein) ER stress cascade, driving apoptosis in cerebral organoids. Pharmacological inhibition of ER stress by pre-treating cerebral organoids with the ER stress inhibitor 4-phenylbutyric acid prior to soman exposure attenuated apoptotic signaling and downregulated GRP78, ATF6 and CHOP expression. Parallel in vivo validation utilized a rat model with subcutaneous soman exposure, focusing on hippocampal and striatal ER stress markers. Consistent with the in vitro findings, soman-exposed rats exhibited marked ER stress activation in brain regions critical for neurotoxicity. This study establishes ER stress as a key contributor to soman-induced neurotoxicity and highlights cerebral organoids as a physiologically relevant model for organophosphorus compound research. We propose ER stress modulation as a potential therapeutic strategy to mitigate neurotoxic outcomes.
Keywords: ATF6; ER stress; cerebral organoids; organophosphates; soman.
© 2025 The Author(s). FEBS Open Bio published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Soltaninejad K and Shadnia S (2014) History of the use and epidemiology of organophosphorus poisoning. In Basic and Clinical Toxicology of Organophosphorus Compounds (Balali‐Mood M and Abdollahi M, eds), pp. 25–44. Springer, London.
-
- Mercey G, Verdelet T, Renou J, Kliachyna M, Baati R, Nachon F, Jean L and Renard P‐Y (2012) Reactivators of acetylcholinesterase inhibited by organophosphorus nerve agents. Acc Chem Res 45, 756–766. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

