Hidradenitis Suppurativa Symptom Daily Diary (HSSDD) and Questionnaire (HSSQ): Psychometric Validation and Interpretation Threshold Derivation Using Phase 3 Study Data
- PMID: 40153232
- PMCID: PMC12033140
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-025-01346-w
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Symptom Daily Diary (HSSDD) and Questionnaire (HSSQ): Psychometric Validation and Interpretation Threshold Derivation Using Phase 3 Study Data
Abstract
Introduction: Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterised by painful skin lesions which negatively impact patients' physical and mental wellbeing. The HS Symptom Daily Diary (HSSDD) and HS Symptom Questionnaire (HSSQ) are patient-reported outcome (PRO) tools capturing patient-perceived severity of HS symptoms. Here, we report the psychometric properties of HSSDD and HSSQ along with score interpretation thresholds.
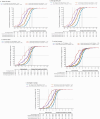
Methods: Pooled data from patients with moderate to severe HS in two phase 3 studies (BE HEARD I II) were analysed. Test-retest reliability was evaluated using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs). Convergent validity was assessed between the HSSDD (N = 934) and HSSQ (N = 1007) compared with relevant PROs and clinician-reported outcomes (ClinROs) at baseline and Week (Wk)16. Known-groups validity was assessed, comparing HSSDD and HSSQ scores between participant subgroups pre-defined using PRO/ClinRO measures (Patient Global Impression [PGI] of HS severity, Hurley stage, International HS Severity Score System). Responsiveness was evaluated by correlating changes from baseline to Wk16 in HSSDD and HSSQ scores with changes in PGI scales. Clinically meaningful within-patient improvement thresholds were estimated using anchor- and distribution-based analyses. Symptom/impact severity thresholds were estimated using receiver operating characteristic curve analyses.
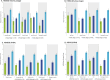
Results: At Wk16, HSSDD and HSSQ completion rates were 70.1% and 90.2%, respectively. Test-retest reliability analyses demonstrated good score reproducibility (ICC: HSSDD: 0.80-0.86; HSSQ: 0.73-0.82). Correlations between HSSDD and HSSQ scores and other PROs/ClinROs were generally consistent with predefined hypotheses, indicating good convergent validity. HSSDD and HSSQ scores discriminated between pre-defined subgroups, confirming known-groups validity. Sixteen-wk changes from baseline in HSSDD and HSSQ scores and anchors were moderately to strongly correlated (> 0.30), establishing responsiveness. Interpretation thresholds for both HSSDD and HSSQ were estimated.
Conclusion: HSSDD and HSSQ item scores demonstrated good psychometric performance in participants with moderate to severe HS. The clinically meaningful severity thresholds defined here could be used to assess treatment efficacy.
Clinical trial registration: NCT04242446; NCT04242498.
Keywords: Bimekizumab; Hidradenitis suppurativa; Patient-reported outcomes; Psychometric validation; Symptoms.
Plain language summary
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition that causes lesions and painful lumps under the skin. HS can affect patients’ lives by causing pain, emotional distress and difficulty completing daily activities. Currently, there are few medications to treat HS. To understand the impact and effectiveness of new treatments, it is important to look beyond clinical outcomes and capture patient experience. To measure the patient’s perspective and more specifically symptom experience, self-completed questionnaires such as the HS Symptom Daily Diary (HSSDD) and HS Symptom Questionnaire (HSSQ) were developed. The HSSDD and HSSQ determine patients’ perspective on the severity of their HS symptoms (pain, itch, smell or odour and drainage or oozing). Two phase 3 trials used HSSDD and HSSQ to investigate patients’ perspective on the severity of their symptoms. We conducted a series of statistical analyses to assess the validity, reliability and robustness of both questionnaires. We found that HSSDD and HSSQ could assess patients’ experience of symptoms. We showed that both questionnaires were sensitive enough to reveal changes over time. Furthermore, both questionnaires were able to distinguish between patient groups with different levels of HS symptom severity. We also established thresholds that will help clinicians determine whether an improvement in a patient’s HSSDD/HSSQ scores are meaningful to the patient. The results from this study show HSSDD and HSSQ are reliable patient-completed questionnaires that could be useful in informing treatment choices.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflicts of interest: John R Ingram: Receives a stipend as Editor‑in‑Chief of the British Journal of Dermatology and an authorship honorarium from UpToDate; consultant for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, ChemoCentryx, Citryll, MoonLake, Novartis, UCB, and Union Therapeutics, and has served on advisory boards for Insmed, Kymera Therapeutics and Viela Bio; co‑copyright holder of HiSQOL©, patient global assessment, and HS-IGA; his department receives income from copyright of the Dermatology Life Quality Instrument (DLQI) and related instruments. Jérémy Lambert, Valerie Ciaravino, Robert Rolleri, Ingrid Pansar, Luke Peterson: Employees and shareholders of UCB. Christopher G Pelligra: Employee of Evidera, a part of ThermoFisher Scientific that receives funding for research from UCB. Linnea Thorlacius: Received speaker honoraria from UCB and is co‑copyright holder of HiSQOL© and HS-IGA. Ethical approval: The study protocol, amendments, and patient informed consent were reviewed by a national, regional, or Independent Ethics Committee (IEC) or Institutional Review Board (IRB). This study was conducted in accordance with the current version of the applicable regulatory and International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH)-Good Clinical Practice (GCP) requirements, the ethical principles that have their origin in the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, and the local laws of the countries involved.
Figures

References
-
- Zouboulis CC, Del Marmol V, Mrowietz U, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: criteria for diagnosis, severity assessment. Classif Dis Eval Dermatol. 2015;231:184–90. - PubMed
-
- Sabat R, Jemec GBE, Matusiak Ł, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6:18. - PubMed
-
- Matusiak Ł. Profound consequences of hidradenitis suppurativa: a review. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:e171–7. - PubMed
-
- Garg A, Neuren E, Cha D, et al. Evaluating patients’ unmet needs in hidradenitis suppurativa: results from the global survey of impact and healthcare needs (VOICE) project. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:366–76. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

