Dynamics of the adhesion complex of the human pathogens Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Mycoplasma genitalium
- PMID: 40153444
- PMCID: PMC11984735
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012973
Dynamics of the adhesion complex of the human pathogens Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Mycoplasma genitalium
Abstract
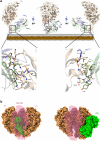
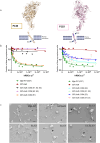
Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Mycoplasma genitalium are bacterial wall-less human pathogens and the causative agents of respiratory and reproductive tract infections. Infectivity, gliding motility and adhesion of these mycoplasmas to host cells are mediated by orthologous adhesin proteins forming a transmembrane adhesion complex that binds to sialylated oligosaccharides human cell ligands. Here we report the cryo-EM structure of M. pneumoniae P1 adhesin bound to the Fab fragment of monoclonal antibody P1/MCA4, which stops gliding and induces detachment of motile cells. The epitope of P1/MCA4 involves residues only from the small C-domain of P1. This epitope is accessible to antibodies only in the "closed conformation" of the adhesion complex and is not accessible in the "open" conformation, when the adhesion complex is ready for attachment to sialylated oligosaccharides. Polyclonal antibodies generated against the large N-domain of P1 or against the whole ectodomain of P40/P90 have little or no effects on adhesion or motility. Moreover, mutations in the highly conserved Engelman motifs found in the transmembrane helix of M. genitalium P110 adhesin also alter adhesion and motility. These results show that antibodies directed to the C-domain of P1 hinder the large conformational rearrangements in this domain required to alternate between the "open" and "closed" conformations of the adhesion complex. Since transition between both conformations is essential to complete the attachment/detachment cycle of the adhesion complex, interfering with the gliding of mycoplasma cells and providing a new potential target to confront M. pneumoniae and M. genitalium infections.
Copyright: © 2025 Vizarraga et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Meyer Sauteur PM, Beeton ML, European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) Study Group for Mycoplasma and Chlamydia Infections (ESGMAC), and the ESGMAC Mycoplasma pneumoniae Surveillance (MAPS) study group. Pneumonia outbreaks due to re-emergence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Lancet Microbe. 2024;5(6):e514. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00406-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mazzolini R, Rodríguez-Arce I, Fernández-Barat L, Piñero-Lambea C, Garrido V, Rebollada-Merino A, et al.. Engineered live bacteria suppress Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in mouse lung and dissolve endotracheal-tube biofilms. Nat Biotechnol. 2023;41(8):1089–98. doi: 10.1038/s41587-022-01584-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

