Dynamic 11C- Para-Aminobenzoic Acid Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography for Visualizing Pulmonary Mycobacteroides abscessus Infections
- PMID: 40153540
- PMCID: PMC12264655
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202409-1792OC
Dynamic 11C- Para-Aminobenzoic Acid Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography for Visualizing Pulmonary Mycobacteroides abscessus Infections
Abstract
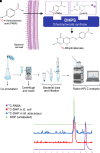
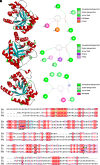
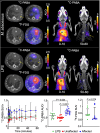
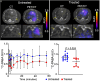
Rationale: Mycobacteroides abscessus infections affect immunocompromised patients and those with underlying pulmonary disease. Conventional imaging cannot distinguish M. abscessus infections from underlying pulmonary disease or sterile inflammation, requiring invasive procedures for definitive diagnosis. Objectives: We evaluated 11C-para-aminobenzoic acid (11C-PABA), a chemically identical radioanalog of PABA, to detect and localize infections due to M. abscessus. Methods: In vitro uptake assays were performed to test the metabolism and accumulation of PABA into M. abscessus reference and clinical isolates. Dynamic 11C-PABA positron emission tomography (PET) was performed in a mouse model of M. abscessus pulmonary infection and in a patient with microbiologically confirmed M. abscessus pulmonary infection (NCT05611905). Measurements and Main Results: 11C-PABA was intracellularly metabolized by M. abscessus to 11C-7,8-dihydropteroate. In addition, the reference strain and all 13 randomly chosen clinical isolates, including 3 resistant to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, rapidly accumulated PABA. No PABA accumulation was noted by heat-inactivated bacteria or mammalian cells. Dynamic 11C-PABA PET in a mouse model of M. abscessus pulmonary infection rapidly distinguished infection from sterile inflammation and also accurately monitored response to antibiotic treatment. Finally, dynamic 11C-PABA PET in a 33-year-old woman with cystic fibrosis and microbiologically confirmed M. abscessus pulmonary infection was safe and demonstrated significantly higher and sustained PET uptake in the affected lesions. Conclusions: 11C-PABA PET is an innovative, clinically translatable, noninvasive, bacteria-specific diagnostic to differentiate M. abscessus infections from underlying pulmonary disease in patients. This tool could also help in monitoring treatment responses and enable precision medicine approaches for patients with complicated infections.
Keywords: molecular imaging; nontuberculous mycobacteria; pathogen specific.
Figures


Comment in
-
Visualizing Pulmonary Mycobacteroides abscessus Infections with 11C Paraaminobenzoic Acid Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography: A Journey, from Bench to Bedside.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2025 Jul;211(7):1122-1124. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202505-1147ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2025. PMID: 40455806 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

