Dual αvβ6 and αvβ1 Inhibition over 12 Weeks Reduces Active Type I Collagen Deposition in Individuals with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Phase 2, Double-Blind, Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial
- PMID: 40153543
- PMCID: PMC12264702
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202410-1934OC
Dual αvβ6 and αvβ1 Inhibition over 12 Weeks Reduces Active Type I Collagen Deposition in Individuals with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Phase 2, Double-Blind, Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
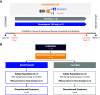
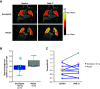
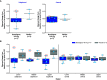
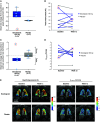
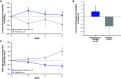
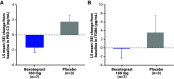
Rationale: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is characterized by excessive deposition of type I collagen. 68Ga-CBP8, a type I collagen positron emission tomography probe, measures collagen accumulation and shows higher collagen deposition in patients with IPF. Bexotegrast (PLN-74809) is an oral, once-daily, dual-selective inhibitor of αvβ6 and αvβ1 integrins under late-stage evaluation for treatment of IPF. Objectives: To evaluate changes in type I collagen in the lungs of participants with IPF after treatment with bexotegrast. Methods: In this phase 2 (NCT05621252), single-center, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, adults with IPF received bexotegrast 160 mg or placebo for 12 weeks. The primary endpoint was the change in whole-lung standardized uptake value of 68Ga-CBP8 positron emission tomography. Changes in lung dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging parameters, FVC, cough severity, and biomarkers of collagen synthesis and progressive disease were also assessed. Measurements and Main Results: Of 10 participants, 7 received bexotegrast and 3 received placebo. At Week 12, the mean change from baseline in the top quartile of 68Ga-CBP8 whole-lung standardized uptake value was -1.2% with bexotegrast versus 6.6% with placebo; the greatest mean changes were observed in subpleural lung regions in both groups (bexotegrast, -3.7%; placebo, 10.3%). Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging showed numerically increased peak enhancement and faster contrast washout rate in bexotegrast-treated participants, suggesting improvements in lung microvasculature and decreased extravascular extracellular volume. Bexotegrast treatment resulted in numerical improvements in FVC, cough severity, and biomarkers. Conclusions: The reduced uptake of 68Ga-CBP8 in the lungs of participants with IPF indicates an antifibrotic effect of bexotegrast, suggesting the potential for favorable lung remodeling. Clinical trial registered with www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT05621252).
Keywords: bexotegrast; collagen type I; fibrotic disease; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; positron emission tomography imaging.
Figures
Comment in
-
Chest Imaging with a Collagen-Binding Probe-A Human Hydroxyproline Assay?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2025 Jul;211(7):1119-1120. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202503-0670ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2025. PMID: 40377671 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lederer DJ, Martinez FJ. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med . 2018;379:797–798. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, et al. ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Committee on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2011;183:788–824. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuhn C, 3rd, Boldt J, King TE, Jr, Crouch E, Vartio T, McDonald JA. An immunohistochemical study of architectural remodeling and connective tissue synthesis in pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis . 1989;140:1693–1703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

