Cost-effectiveness of intrapartum azithromycin to prevent maternal infection, sepsis, or death in low-income and middle-income countries: a modelling analysis of data from a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 40155105
- PMCID: PMC11950424
- DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(24)00517-5
Cost-effectiveness of intrapartum azithromycin to prevent maternal infection, sepsis, or death in low-income and middle-income countries: a modelling analysis of data from a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is one of the leading causes of maternal mortality globally. In 2023, the Azithromycin Prevention in Labor Use (A-PLUS) trial showed intrapartum azithromycin for women planning a vaginal birth reduced the risk of maternal sepsis or death and infection. We aimed to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of intrapartum azithromycin for pregnant people planning a vaginal birth in low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs) using A-PLUS trial data.
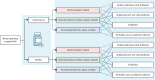
Methods: We compared the benefits and costs of intrapartum azithromycin versus standard care across 100 000 model simulations using data from the A-PLUS trial and a probabilistic decision tree model that included 24 mutually exclusive scenarios. A-PLUS was a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that enrolled 29 278 women in labour at 28 weeks' gestation or more at eight sites in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Zambia, Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, and Guatemala. Women randomly assigned to azithromycin received a single intrapartum 2 g oral dose. In this cost-effectiveness analysis, we considered the cost of azithromycin treatment and its effects on a composite outcome of maternal infection, sepsis, or death and its individual components, and health-care use. Our analysis had a health-care sector perspective. We summarised results as an average and 95% CI of the model simulations. We also conducted sensitivity analyses. A-PLUS was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT03871491.
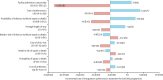
Findings: In model simulations, intrapartum azithromycin resulted in 1592·0 (95% CI 1139·7 to 2024·1) cases of maternal infection, sepsis, or death averted per 100 000 pregnancies, yielding 248·5 (95·3 to 403·7) facility readmissions averted, 866·8 (537·8 to 1193·2) unplanned clinic visits averted, and 1816·2 (1324·5 to 2299·7) antibiotic regimens averted. Using mean health-care costs across the A-PLUS sites, intrapartum azithromycin resulted in net savings of US$32 661 (-52 218 to 118 210) per 100 000 pregnancies and 13·2 (8·3 to 17·9) disability-adjusted life-years averted. The cost of facility readmission, cost of azithromycin, and probability of infection had the greatest impact on the incremental cost.
Interpretation: In most cases, intrapartum azithromycin is a cost-saving intervention for the prevention of maternal infection, sepsis, or death in LMICs. This evidence supports global consideration of intrapartum azithromycin as an economically efficient preventive therapy to reduce infection, sepsis, or death among women planning a vaginal birth in LMICs.
Funding: Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health through the Maternal, Newborn, and Child Health Discovery and Tools Initiative of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation TRANSLATIONS: For the French and Spanish translations of the abstract see Supplementary Materials section.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests All authors other than MK-T received National Institute for Child Health and Human Development grant funding for this work; AT received additional funding from Mirvie, the American Heart Association, and Pfizer for research related to this work.
Figures
Comment in
-
The promise of antibiotic-led reduction in maternal infection.Lancet Glob Health. 2025 Apr;13(4):e604-e605. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(25)00051-8. Lancet Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40155093 No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO Trends in maternal mortality 2000 to 2020: estimates by WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, World Bank Group and UNDESA/Population Division. Feb 23, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240068759
-
- WHO Maternal mortality. April 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/maternal-mortality
-
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2023: special edition. July, 2023. https://desapublications.un.org/publications/sustainable-development-goa...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

