Nanotechnology-based drug delivery system for the diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer
- PMID: 40155504
- PMCID: PMC11953507
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02062-9
Nanotechnology-based drug delivery system for the diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer
Abstract
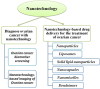
Current research in nanotechnology is improving or developing novel applications that could improve disease diagnosis or treatment. This study highlights several nanoscale drug delivery technologies, such as nano micelles, nanocapsules, nanoparticles, liposomes, branching dendrimers, and nanostructured lipid formulations for the targeted therapy of ovarian cancer (OC), to overcome the limitations of traditional delivery. Because traditional drug delivery to malignant cells has intrinsic flaws, new nanotechnological-based treatments have been developed to address these conditions. Ovarian cancer is the most common gynecological cancer and has a higher death rate because of its late diagnosis and recurrence. This review emphasizes the discipline of medical nanotechnology, which has made great strides in recent years to solve current issues and enhance the detection and treatment of many diseases, including cancer. This system has the potential to provide real-time monitoring and diagnostics for ovarian cancer treatment, as well as simultaneous delivery of therapeutic agents.
Keywords: Anticancer drug; Drug delivery; Drug targeting; Nanotechnology; Ovarian cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nanotechnological approaches for diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer: a review of recent trends.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):3218-3232. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2132032. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 36259505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology in ovarian cancer: Diagnosis and treatment.Life Sci. 2021 Feb 1;266:118914. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118914. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33340527 Review.
-
Nanotechnology: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(19):1-43. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074489 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting and destroying cancer cells in more than one way with noble metals and different confinement properties on the nanoscale.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Nov 20;45(11):1854-65. doi: 10.1021/ar2003122. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22546051 Free PMC article.
-
New trends in diagnosing and treating ovarian cancer using nanotechnology.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Apr 4;11:1160985. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1160985. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37082219 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wnt signal pathways: new mechanistic approaches and clinical horizons in cancer therapy.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 8;42(8):314. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02868-1. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40629193 Review.
-
Recent strategies in diagnosis, screening, prevention, and treatment of breast cancer in young women.Discov Oncol. 2025 Aug 11;16(1):1532. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03180-0. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40789789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of ovarian cancer: From the past to the new era (Review).Oncol Lett. 2025 Jun 3;30(2):384. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.15130. eCollection 2025 Aug. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40535104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the Role of the microRNA-Mediated Regulation of Actin-Binding Proteins in Ovarian Cancer: A Narrative Review.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;17(14):2315. doi: 10.3390/cancers17142315. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723199 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ziller C, Lincet H, Muller CD, Staedel C, Behr JP, Poulain L. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21cip1/waf1 enhances the cytotoxicity of ganciclovir in HSV-tk transfected ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2004;212(1):43–52. 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.03.048. - PubMed
-
- Eishi A, Rahimi E, Akhavan S, Shahgaibi S, Fariba F. Cancer during pregnancy: a review of 10 years of experience. Pak J Biol Sci. 2012;15(7):341–6. 10.3923/pjbs.2012.341.346. - PubMed
-
- Gidwani B, Vyas A. The potentials of nanotechnology-based drug delivery system for treatment of ovarian cancer. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2015;43(4):291–7. 10.3109/21691401.2013.853179. - PubMed
-
- Satpathy M, Wang L, Zielinski RJ, Qian W, Wang YA, Mohs AM, Kairdolf BA, Ji X, Capala J, Lipowska M, Nie S. Targeted drug delivery and image-guided therapy of heterogeneous ovarian cancer using HER2-targeted theranostic nanoparticles. Theranostics. 2019;9(3):778–95. 10.7150/thno.29964. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Talluri S, Malla RR. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) for diagnosis and treatment of breast, ovarian and cervical cancers. Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(12):942–5. 10.2174/1389200220666191016124958. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
