Identification and validation of molecular subtypes and prognostic models in patients with kidney cancer based on differential genes based on B cells: a multiomics analysis
- PMID: 40155904
- PMCID: PMC11951520
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-025-13923-5
Identification and validation of molecular subtypes and prognostic models in patients with kidney cancer based on differential genes based on B cells: a multiomics analysis
Abstract
Background: B cells play a variety of complex roles in cancer, both promoting cancer progression and enhancing anti-tumor immune responses, but their mechanism of action in kidney cancer has not been elucidated.
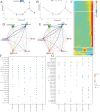
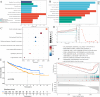
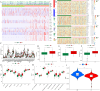
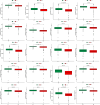
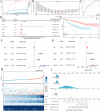
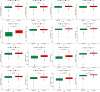
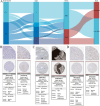
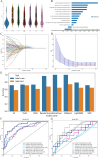
Results: We collected kidney cancer sample data from the GEO database and TCGA database, mapped the single-cell landscape inside kidney cancer tissue, identified 25 B-cell-related genes, and based on this, identified related molecular subtypes of kidney cancer patients, and explored their internal microenvironment characteristics. Finally, we constructed a 6-gene biological prognostic model that can be used to predict survival in patients with renal cancer, and we further validated the predictive performance of the model based on imaging omics. It is worth mentioning that the structural patterns and functional sites of 6 model gene transcription proteins were also mined.
Conclusions: Overall, we explored for the first time the profound role of B cells in kidney cancer and developed a bio-predictive model based on B cell-related genes, providing scientific guidance for personalized treatment of kidney cancer patients.
Keywords: B cell; Immune microenvironment; Multiomics; Prognostic model; Renal carcinoma.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Integrated Multi-Omics Analysis Unveils Distinct Molecular Subtypes and a Robust Immune-Metabolic Prognostic Model in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 28;26(7):3125. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073125. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243888 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of 4-genes model in papillary renal cell tumor microenvironment based on comprehensive analysis.BMC Cancer. 2021 May 17;21(1):553. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08319-0. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33993869 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of prognostic biomarkers in ccRCC: immune-stromal score and survival prediction.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jan 27;25(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13534-0. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39871215 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics identification of a polyamine metabolism related signature for hepatocellular carcinoma and revealing tumor microenvironment characteristics.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 22;16:1570378. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1570378. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40330470 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the role of PANoptosis-related genes in breast cancer: an integrated study by multi-omics analysis and machine learning algorithms.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025 May;211(1):35-50. doi: 10.1007/s10549-025-07620-x. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 39870964
References
-
- González-Garza R, et al. Biomarkers for evaluating the clinical response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in renal cell carcinoma (Review). Oncol Rep. 2024;52(6):1–0. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

