DEMINERS enables clinical metagenomics and comparative transcriptomic analysis by increasing throughput and accuracy of nanopore direct RNA sequencing
- PMID: 40155949
- PMCID: PMC11954306
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-025-03536-3
DEMINERS enables clinical metagenomics and comparative transcriptomic analysis by increasing throughput and accuracy of nanopore direct RNA sequencing
Abstract
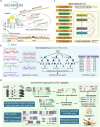
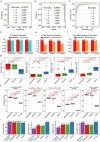
Nanopore direct RNA sequencing (DRS) is a powerful tool for RNA biology but suffers from low basecalling accuracy, low throughput, and high input requirements. We present DEMINERS, a novel DRS toolkit combining an RNA multiplexing workflow, a Random Forest-based barcode classifier, and an optimized convolutional neural network basecaller with species-specific training. DEMINERS enables accurate demultiplexing of up to 24 samples, reducing RNA input and runtime. Applications include clinical metagenomics, cancer transcriptomics, and parallel transcriptomic comparisons, uncovering microbial diversity in COVID-19 and m6A's role in malaria and glioma. DEMINERS offers a robust, high-throughput solution for precise transcript and RNA modification analysis.
Keywords: Basecalling; Demultiplex; Machine learning; Nanopore direct RNA sequencing; RNA modification.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Tumour sample collection and the study design were approved by the Biomedical Research Ethics Committee of West China Hospital (Approval number: 2020.837). The research on COVID-19 specimens was approved by the Biomedical Research Ethics Committee of West China Hospital (Approval number 2020.100, 2020.193 and 2020.267). The swabs were obtained for routine diagnostic purposes, and the remaining RNA samples were provided for research. Written consents were obtained from all patients. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: Sichuan University has filed patent applications for the methods described herein, with L.C., J.-wL., J.G., J.S., C.T., L.L., and C.C. listed as inventors. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Hussain S. Native RNA-Sequencing Throws its Hat into the Transcriptomics Ring. Trends Biochem Sci. 2018;43:225–7. - PubMed
-
- Workman RE, Tang AD, Tang PS, Jain M, Tyson JR, Razaghi R, Zuzarte PC, Gilpatrick T, Payne A, Quick J, Sadowski N, Holmes N, de Jesus JG, Jones KL, Soulette CM, Snutch TP, Loman N, Paten B, Loose M, Simpson JT, Olsen HE, Brooks AN, Akeson M, Timp W. Nanopore native RNA sequencing of a human poly(A) transcriptome. Nat Methods. 2019;16:1297–305. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

