Diagnostic accuracy of plasma p-tau217/Aβ42 for Alzheimer's disease in clinical and community cohorts
- PMID: 40156286
- PMCID: PMC11953589
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70038
Diagnostic accuracy of plasma p-tau217/Aβ42 for Alzheimer's disease in clinical and community cohorts
Abstract
Introduction: This study was undertaken to evaluate the diagnostic performance of a novel plasma phosphorylated tau (p-tau) 217/amyloid beta (Aβ) 42 ratio test for Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Methods: The diagnostic performance of the Lumipulse G plasma p-tau217/Aβ42 ratio was evaluated using Aβ and tau positron emission tomography (PET) as reference standards in a clinic cohort (n = 391) and a community cohort (n = 121).
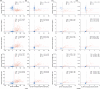
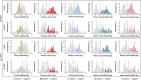
Results: Plasma p-tau217/Aβ42 exhibited high performance for abnormal statuses of Aβ PET (area under the curve [AUC]: 0.963 to 0.966) and tau PET (AUC: 0.947 to 0.974), which were clinically equivalent to those of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) p-tau181/Aβ42 and Aβ42/Aβ40 and higher than those of blood p-tau217, Aβ42/Aβ40, p-tau181, and p-tau181/Aβ42 in both clinic and community cohorts. Applying a two-cutoff approach improved the specificity without reducing sensitivity. The p-tau217/Aβ42 ratio had a lower intermediate percentage than p-tau217 alone in both clinic (10.6% vs 13.0%) and community (16.5% vs 31.4%) cohorts.
Discussion: Plasma p-tau217/Aβ42 has high performance in detecting cerebral AD pathologies, thus offering a promising tool for clinical diagnosis and community screening of AD.
Highlights: Lumipulse G plasma p-tau217 and the p-tau217/Aβ42 ratio accurately identified abnormal Aβ and tau PET statuses in both clinical and community cohorts. The performance of plasma p-tau217 and p-tau217/Aβ42 ratio were equivalent to CSF tests. Plasma p-tau217/Aβ42 ratio outperformed p-tau217 alone in identifying Aβ PET positivity, and this superiority is more obvious in the community cohort, suggesting an advantage in the early diagnosis of AD. Two cut points of p-tau217/Aβ42 were established in the Chinese population for clinical laboratory and community screening uses.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Lumipulse; amyloid positron emission tomography; blood biomarker; diagnosis; p‐tau217/Aβ42; two‐cutoff approach.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
H.Z. has served on scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for AbbVie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Amylyx, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, Cognito Therapeutics, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, LabCorp, Merry Life, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave and has given lectures at symposia sponsored by Alzecure, Biogen, Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Roche. The other authors declare no competing interests. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting information.
Figures




References
-
- 2023 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2023;19(4):1598‐1695. - PubMed
-
- Li WW, Shen YY, Tian DY, et al. Brain amyloid‐beta deposition and blood biomarkers in patients with clinically diagnosed Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;69(1):169‐178. - PubMed
-
- van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, et al. Lecanemab in early Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(1):9‐21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023YFC3605400/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 92249305/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81930028/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82422027/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82171197/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2024GGXM003/Chongqing Science and Technology Bureau and the Health Commission
- 2023B1515020113/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Science Foundation
- S241101004-1/Shenzhen Bay Laboratory
- 2023-00356/Swedish Research Council supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council
- 2022-01018/Swedish Research Council supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council
- 2019-02397/Swedish Research Council supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council
- 101053962/European Union's Horizon Europe Research and Innovation Programme
- ALFGBG-71320/Swedish State Support for Clinical Research
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

