Plasma Biomarkers and Disease Prognosis in Mild Cognitive Impairment with Lewy Bodies
- PMID: 40156325
- PMCID: PMC12160992
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.30181
Plasma Biomarkers and Disease Prognosis in Mild Cognitive Impairment with Lewy Bodies
Abstract
Background: Little is known about the prognostic value of plasma biomarkers in mild cognitive impairment with Lewy bodies (MCI-LB).
Objectives: To investigate the association of four plasma biomarkers with disease progression in MCI.
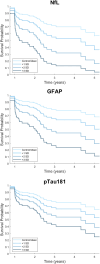
Methods: Plasma amyloid-beta (Aβ)42/40, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), neurofilament light (NfL), and phosphorylated tau 181 (pTau181) were measured at baseline in a longitudinal MCI cohort (n = 131).
Results: Baseline plasma NfL was associated with increased risk of dementia/death in the entire cohort. In MCI-LB, baseline plasma NfL, GFAP, and pTau181 were associated with increased risk of dementia/death and increased cognitive decline measured by the Addenbrooke's Cognitive Examination-Revised.
Conclusions: pTau181, GFAP, and NfL are associated with more rapid disease progression in MCI-LB and, with further validation, could be useful to support prognosis and stratification for clinical practice and treatment trials. Further work, including clinicopathological studies, is needed to understand the biological correlates of these markers in MCI-LB. © 2025 The Author(s). Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; dementia with Lewy bodies; mild cognitive impairment; plasma biomarkers; prognosis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

