Emerging themes and future directions in space radiation health research: a bibliometric exploration from 2013 to 2022
- PMID: 40156613
- PMCID: PMC12049392
- DOI: 10.1007/s00411-025-01115-5
Emerging themes and future directions in space radiation health research: a bibliometric exploration from 2013 to 2022
Abstract
The impact of space radiation on health (SRHE) is extensive and significantly influences public health and space operations, making it essential to analyze global collaboration networks and track developmental trends over the last decade. However, bibliometric analysis in this area remains limited. This study aims to outline publication trends, citation patterns, major journals, key authors, institutional and national collaborations, and to explore emerging themes and future directions. A bibliometric analysis was conducted using CiteSpace, Bibliometrix in R, and VOSviewer on SRHE research from the Web of Science Core Collection up to November 12, 2023. The analysis included 390 records from 4,857 journals, involving 1,918 authors across 701 institutions in 53 countries. The predominant publications were Articles and Review Articles in Life Sciences and Biomedicine, with a notable publication surge in 2020. The most cited work was by Li et al. (2017), with Cucinotta F.A. as the most prolific author. The USA led in publications, citations, and collaboration strength, followed by Germany and China. Key journals include Radiation Research, Plos One, Life Sciences in Space Research, and Health Physics. Research has focused on radiation exposure effects, DNA damage repair, astronaut health risks, and radiation protection, with emerging trends in microgravity, astrobiology, and lifespan research, which examines the biological, psychological, and social aspects of aging and the entire life course, aiming to understand and extend the health span-the period of life free from chronic diseases and age-related disabilities-rather than just the total lifespan. Future research may benefit from focusing on personalized radiation protection, exploring biological mechanisms, and embracing technological innovations, based on the trends observed in this study.
Keywords: Bibliometrix; CiteSpace; Health effects; Radiation protection; Space radiation; VOSviewer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: Not applicable. Consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


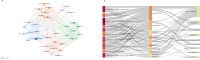
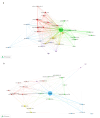
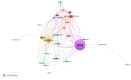

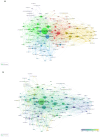

Similar articles
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Emerging research themes in maternal hypothyroidism: a bibliometric exploration.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 26;15:1370707. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1370707. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38596686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometric analysis of laryngeal cancer treatment literature (2003-2023).Heliyon. 2024 Dec 16;11(1):e40832. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40832. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39811326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping the Evolution of Digital Health Research: Bibliometric Overview of Research Hotspots, Trends, and Collaboration of Publications in JMIR (1999-2024).J Med Internet Res. 2024 Oct 17;26:e58987. doi: 10.2196/58987. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39419496 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of E-cigarette-A bibliometric analysis during 2010-2022.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 1;10:928059. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.928059. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35979459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambrožová I, Brabcová KP, Kubančák J et al (2017) Cosmic radiation monitoring at low-Earth orbit by means of thermoluminescence and plastic nuclear track detectors. Radiat Meas 106:262–266. 10.1016/j.radmeas.2016.12.004
-
- Babu B, Pawar S, Mittal A et al (2023) Nanotechnology enabled radioprotectants to reduce space radiation-induced reactive oxidative species. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 15:e1896. 10.1002/wnan.1896 - PubMed
-
- Cao X (2022) Research progress on the effects of microgravity and space radiation on astronauts’ health and nursing measures. Open Astronomy 31:300–309. 10.1515/astro-2022-0038
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

