Integrative structural analysis of NF45-NF90 heterodimers reveals architectural rearrangements and oligomerization on binding dsRNA
- PMID: 40156862
- PMCID: PMC11952958
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf204
Integrative structural analysis of NF45-NF90 heterodimers reveals architectural rearrangements and oligomerization on binding dsRNA
Abstract
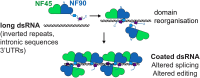
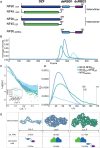
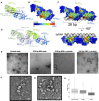
Complexes of nuclear factors 45 and 90 (NF45-NF90) play a multitude of roles in co- and post-transcriptional RNA processing, including regulating adenosine-to-inosine editing, cassette exon and back splicing, and splicing fidelity. NF45-NF90 complexes recognize double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and, in human cells, primarily interact with Alu inverted repeats (AluIRs) that are commonly inserted into introns and other non-coding RNA regions. Intronic AluIRs of ∼300 bp can regulate splicing outcomes, such as generation of circular RNAs. We examined domain reorganization of NF45-NF90 domains on dsRNAs exceeding 50 bp to gain insight into its RNA recognition properties on longer dsRNAs. Using a combination of phylogenetic analysis, solution methods (including small angle X-ray scattering and quantitative cross-linking mass spectrometry), machine learning, and negative stain electron microscopy, we generated a model of NF45-NF90 complex formation on dsRNA. Our data reveal that different interactions of NF45-NF90 complexes allow these proteins to coat long stretches of dsRNA. This property of the NF45-NF90 complex has important implications for how long, nuclear dsRNAs are recognized in the nucleus and how this might promote (co)-regulation of specific RNA splicing and editing events that shape the mammalian transcriptome.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

