Real-world risk of recurrence and treatment outcomes with adjuvant endocrine therapy in patients with stage II-III HR+/HER2- early breast cancer
- PMID: 40157276
- PMCID: PMC11995083
- DOI: 10.1016/j.breast.2025.104437
Real-world risk of recurrence and treatment outcomes with adjuvant endocrine therapy in patients with stage II-III HR+/HER2- early breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Despite adjuvant endocrine therapy (ET), recurrence is still a concern for patients with HR+/HER2- early breast cancer (EBC). We assessed recurrence risk in real-world patients with stage II/III HR+/HER2- EBC treated with adjuvant ET.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted using the ConcertAI Patient360 database (January 1995 to April 2021) of patients with stage II/III HR+/HER2- EBC ≥18 years who underwent surgery and received adjuvant ET. Risk of recurrence was assessed using invasive disease-free survival (iDFS) with adapted STEEP criteria. An ET subanalysis evaluated iDFS, distant disease-free survival, and overall survival in patients receiving adjuvant non-steroidal aromatase inhibitors (NSAI) vs tamoxifen.
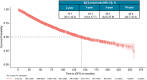
Results: In the full analysis cohort (N = 3133), the risk of an iDFS event was 26.1 % at 5 years, rising to 45.0 % at 10 years. Among patients with stage II disease, the risk of an iDFS event at 5 and 10 years was 22.7 % and 40.5 %, respectively; stage III 5- and 10-year risk was 40.4 % and 62.9 %. Patients with node-negative disease had 5- and 10-year risks of 22.1 % and 36.9 %, respectively; node-positive 5- and 10-year risk was 28.9 % and 49.4 %. ET subanalysis showed improved iDFS with NSAI ± ovarian function suppression vs tamoxifen ± ovarian function suppression (HR, 0.83; 95 % CI, 0.69-0.98; p = 0.031); this trend was observed regardless of menopausal status.
Conclusions: This real-world study highlights the considerable risk of recurrence with adjuvant ET in patients with stage II or III HR+/HER2- EBC (including node-negative disease) and confirms the need for improved treatment options.
Keywords: Adjuvant therapy; HR+/HER2-early breast cancer; Real world; Risk of recurrence.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest J. O'Shaughnessy reports personal fees from AbbVie, Agendia, Amgen, Aptitude, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eisai, G1 Therapeutics, Genentech, Immunome, Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Lilly, Merck, Myriad, Novartis, Odonate Therapeutics, Pfizer, Puma, Prime, Roche, Seattle Genetics, Syndax, Carrick Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead Sciences, Ontada, Pierre Fabre, Samsung, Sanofi. S. Tolaney reports grant funding to institution and personal fees from Eli Lilly, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Merck, Pfizer, Genentech/Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Sanofi, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Menarini/Stemline; grant funding to institution from Exelixis, Nanostring, OncoPep; personal fees from Seattle Genetics, Arvinas, Cullinan Oncology, eFFECTOR, CytomX, Sumitovant Biopharma, Natera, Tango Therapeutics, SystImmune, Hengrui USA, Blueprint Medicines, Reveal Genomics, Umoja Biopharma, Zentalis, Zymeworks, Circle Pharma, Bayer, Incyte Corp, Aadi Biopharma. D. Yardley reports research funding grants to institution from Ambrx, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BIOMARIN, Biothera Pharmaceuticals, Clovis Pharma, Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Lilly, Roche/Genentech, G1 Therapeutics, Incyte, Innocrin Pharmaceuticals, MacroGenics, MedImmune, Medivation, Merck, Merrimack Pharmaceuticals, Nektar Therapeutics, Novartis, NSABP, Polyphor, Stemline Therapeutics, UT Southwestern; consulting/advisory fees to institution from AstraZeneca, G1 Therapeutics, Gilead Sciences, Immunomedics, Integra Connect, Novartis, Sanofi-Aventis, Stemline Therapeutics. L. Hart reports grants to institution and personal fees from Novartis. P. Razavi reports institutional grants from Grail/Illumina, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Epic Sciences, Invitae/ArcherDx, Tempus, Inivata, BioTheranostics; personal fees from Novartis, AstraZeneca, Epic Sciences, Tempus, Inivata, Foundation Medicine, Pfizer, Daiichi Sankyo, Natera, Paige.AI, SAGA Diagnostics. P. Fasching reports personal fees from Novartis, Pfizer, Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, Eisai, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Lilly, Pierre Fabre, SeaGen, Roche, Agendia, Sanofi Aventis, Gilead, Mylan, Menarini, Medac, Veracyte, Guardant Health; institutional grants from Biontech, Pfizer, Cepheid. W. Janni reports personal fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Seagen, Gilead; employment from Universitätsklinikum Ulm; speaker fees to institution from Novartis, GSK, Sanofi, Amgen, Roche, Lilly; chair of AGO Breast Council. L. Schwartzberg reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Genentech, Novartis, Pfizer, Seagen, Merck, Spectrum, Napo, Amgen. J. Kim reports employment from Genesis Research, whom Novartis has paid fees for consulting. M. Akdere, C. McDermott report employment and stock ownership from Novartis. A. Khakwani reports employment and stock ownership from Novartis; prior employment from Imperial Brands PLC. P. Pathak reports employment and stock ownership from Novartis. S. Graff reports personal fees from Novartis, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Lilly, Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, Gilead Sciences, The Academy for Healthcare Learning, DAVA Oncology, MJH Life Sciences, WebMD/Medscape, IntegrityCE, MedPage Today, MedIQ, Medical Educator Consortium, Research to Practice; consulting fees paid to institution from Seagen; other from HCA Healthcare; research grants to institution from Daiichi Sankyo, Novartis, AstraZeneca.
Figures

References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. Breast Cancer. March 2025 V3 2025. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

