Contrast-enhanced MRI-based intratumoral heterogeneity assessment for predicting lymph node metastasis in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40159327
- PMCID: PMC11955437
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-025-01956-0
Contrast-enhanced MRI-based intratumoral heterogeneity assessment for predicting lymph node metastasis in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Erratum in
-
Correction: Contrast-enhanced MRI-based intratumoral heterogeneity assessment for predicting lymph node metastasis in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Insights Imaging. 2025 May 15;16(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13244-025-01973-z. Insights Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40372613 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objectives: To develop and validate a contrast-enhanced MRI-based intratumoral heterogeneity (ITH) model for predicting lymph node (LN) metastasis in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
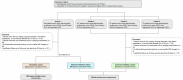
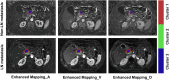
Methods: Lesions were encoded into different habitats based on enhancement ratios at arterial, venous, and delayed phases of contrast-enhanced MRI. Habitat models on enhanced ratio mapping and single sequences, radiomic models, and clinical models were developed for evaluating LN metastasis. The performance of the models was evaluated via different metrics. Additionally, patients were stratified into high-risk and low-risk groups based on an ensembled model to assess prognosis after adjuvant therapy.
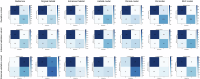
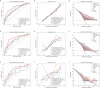
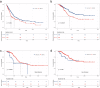
Results: We developed an ensembled radiomics-habitat-clinical (RHC) model that integrates radiomics, habitat, and clinical data for precise prediction of LN metastasis in PDAC. The RHC model showed strong predictive performance, with area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.805, 0.779, and 0.615 in the derivation, internal validation, and external validation cohorts, respectively. Using an optimal threshold of 0.46, the model effectively stratified patients, revealing significant differences in recurrence-free survival and overall survival (OS) (p = 0.004 and p < 0.001). Adjuvant therapy improved OS in the high-risk group (p = 0.004), but no significant benefit was observed in the low-risk group (p = 0.069).
Conclusion: We developed an MRI-based ITH model that provides reliable estimates of LN metastasis for resectable PDAC and may offer additional value in guiding clinical decision-making.
Critical relevance statement: This ensemble RHC model facilitates preoperative prediction of LN metastasis in resectable PDAC using contrast-enhanced MRI. This offers a foundation for enhanced prognostic assessment and supports the management of personalized adjuvant treatment strategies.
Key points: MRI-based habitat models can predict LN metastasis in PDAC. Both the radiomics model and clinical characteristics were useful for predicting LN metastasis in PDAC. The RHC models have the potential to enhance predictive accuracy and inform personalized therapeutic decisions.
Keywords: Habitat; Lymph node metastasis; Magnetic resonance imaging; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study received approval from the Institutional Review Board of Zhongshan Hospital (approval no. B2024-250R). Due to its retrospective design, the requirement for obtaining written informed consent was waived. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: Z.C. is affiliated with Shanghai United Imaging Intelligence Co. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Feasibility of a CT-based lymph node radiomics nomogram in detecting lymph node metastasis in PDAC patients.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 5;12:992906. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.992906. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36276058 Free PMC article.
-
Applying a radiomics-based strategy to preoperatively predict lymph node metastasis in the resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.J Xray Sci Technol. 2020;28(6):1113-1121. doi: 10.3233/XST-200730. J Xray Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 33074215
-
Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Based on a Radiomics Nomogram of Dual-Parametric MRI Imaging.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 6;12:927077. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.927077. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35875061 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-operative radiomics model for prognostication in resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma with external validation.Eur Radiol. 2022 Apr;32(4):2492-2505. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08314-w. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34757450
-
Radiomics and deep learning models for CT pre-operative lymph node staging in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Radiol. 2024 Jul;176:111510. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2024.111510. Epub 2024 May 18. Eur J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38781919
References
-
- Bardeesy N, DePinho RA (2002) Pancreatic cancer biology and genetics. Nat Rev Cancer 2:897–909 - PubMed
-
- Hu ZI, O Reilly EM (2024) Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 21:7–24 - PubMed
-
- Springfeld C, Ferrone CR, Katz MHG et al (2023) Neoadjuvant therapy for pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 20:318–337 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

