SGA-Driven feature selection and random forest classification for enhanced breast cancer diagnosis: A comparative study
- PMID: 40159513
- PMCID: PMC11955515
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-95786-1
SGA-Driven feature selection and random forest classification for enhanced breast cancer diagnosis: A comparative study
Abstract
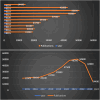
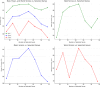
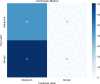
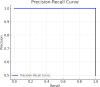
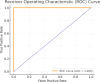
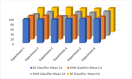
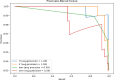
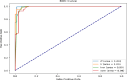
In this study, we propose a novel approach for breast cancer classification that integrates the Seagull Optimization Algorithm (SGA) for feature selection with the Random Forest (RF) classifier for effective data classification. The novelty of our approach lies in the first-time application of SGA for gene selection in breast cancer diagnosis, where SGA systematically explores the feature space to identify the most informative gene subsets, thereby improving classification accuracy and reducing computational complexity. The selected features are subsequently classified using RF, known for its robustness and high accuracy in handling complex datasets. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we compared it with other classifiers, including Linear Regression (LR), Support Vector Machine (SVM), and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN). The proposed SGA-RF combination achieved a best mean accuracy of 99.01% with 22 genes, outperforming other methods and demonstrating consistent performance across varying feature subsets. The mean accuracies ranged from 85.35 to 94.33%, highlighting a balance between feature reduction and classification accuracy. Future work will explore the integration of other nature-inspired algorithms and deep learning models to further enhance performance and clinical applicability.
Keywords: Cancer classification; High dimensional data; Random forest; Seagull optimization algorithm.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Consent to participate: Not applicable. This study does not involve human participants requiring consent. Consent to publish: Not applicable. The manuscript does not include any individual person’s data in any form requiring consent.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Electromagnetic Interaction Algorithm (EIA)-Based Feature Selection With Adaptive Kernel Attention Network (AKAttNet) for Autism Spectrum Disorder Classification.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2025 Aug;85(5):e70034. doi: 10.1002/jdn.70034. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40751377
-
A novel double machine learning approach for detecting early breast cancer using advanced feature selection and dimensionality reduction techniques.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22971. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06426-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596255 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning for detection of diffusion abnormalities-related respiratory changes among normal, overweight, and obese individuals based on BMI and pulmonary ventilation parameters: an observational study.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12911-025-03064-x. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025. PMID: 40598421 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
Cited by
-
GNNs surpass transformers in tumor medical image segmentation.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 5;15(1):19842. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00002-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40473649 Free PMC article.
-
Fusing wrist pulse and ECG data for enhanced identification of coronary heart disease and its complications.Front Physiol. 2025 Jul 29;16:1628309. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1628309. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40800731 Free PMC article.
-
AI driven automation for enhancing sustainability efforts in CDP report analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 7;15(1):24266. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07584-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40624129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yaqoob, A., Verma, N. K. & Aziz, R. M. Improving breast cancer classification with mRMR + SS0 + WSVM: a hybrid approach. Multimed Tools Appl.10.1007/s11042-024-20146-6 (2024).
-
- Bhat, A. S. et al. Cancer initiation and progression: A comprehensive review of carcinogenic substances, Anti-Cancer therapies, and regulatory frameworks. Asian J. Res. Biochem.14 (4), 111–125. 10.9734/ajrb/2024/v14i4300 (2024).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

