Sodium Hyaluronate-PDGF Repairs Cartilage and Subchondral Bone Microenvironment via HIF-1α-VEGF-Notch and SDF-1-CXCR4 Inhibition in Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 40159624
- PMCID: PMC11955409
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70515
Sodium Hyaluronate-PDGF Repairs Cartilage and Subchondral Bone Microenvironment via HIF-1α-VEGF-Notch and SDF-1-CXCR4 Inhibition in Osteoarthritis
Abstract
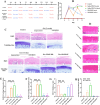
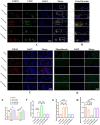
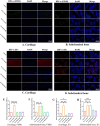
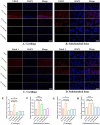
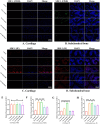
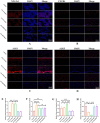
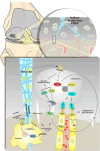
Chronic degenerative changes in cartilage and subchondral bone that lead to instability of the cartilage microenvironment are essential for the development of osteoarthritis (OA) in the old. Synchronous repair of cartilage and subchondral bone may be a key strategy for OA treatment. PDGF-BB effectively promoted chondrocyte regeneration and angiogenesis. However, the mechanisms by which PDGF-BB affects subchondral bone and the delivery of PDGF-BB to the joint cavity need to be further explored. In this study, we used sodium hyaluronate to deliver PDGF-BB (SH-PDGF) to the joint space and aimed to determine the mechanisms of SH-PDGF in repairing cartilage and subchondral bone and stabilising the cartilage microenvironment. In this research, we determined the pharmacokinetics of PDGF-BB and SH-PDGF in cartilage. Moreover, we investigated the effects of PDGF-BB and SH-PDGF on cartilage and the subchondral bone microenvironment by identifying changes in the HIF-VEGF-Notch axis and SDF-1-CXCR4 axis in an OA rat model. The results showed that PDGF-BB increased cell viability, decreased HIF-1α levels, inhibited inflammation and improved matrix metabolism in osteoarthritic chondrocytes under hyperoxic or hypoxic conditions. We also found that PDGF-BB and SH-PDGF showed similar effects on repairing cartilage and subchondral bone simultaneously. However, SH-PDGF had some advantages over PDGF-BB in prolonging the injection interval and decreasing the injection time. These protective effects were mediated by the inhibition of both the HIF-1α-VEGF-Notch axis and the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis. The underlying mechanisms include the inhibition of HIF-1α-VEGF-Notch-mediated vessel invasion and SDF-1-CXCR4 axis-mediated crosstalk between cartilage and subchondral tissue.
Keywords: cartilage; microenvironment; osteoarthritis; platelet‐derived growth factor; subchondral bone.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of SDF-1α/CXCR4 Signalling in Subchondral Bone Attenuates Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 16;17(6):943. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060943. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. Retraction in: Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 16;25(14):7757. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147757. PMID: 27322244 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
SDF-1/CXCR4 axis coordinates crosstalk between subchondral bone and articular cartilage in osteoarthritis pathogenesis.Bone. 2019 Aug;125:140-150. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.05.010. Epub 2019 May 17. Bone. 2019. PMID: 31108241
-
Inhibition of SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis to Alleviate Abnormal Bone Formation and Angiogenesis Could Improve the Subchondral Bone Microenvironment in Osteoarthritis.Biomed Res Int. 2021 May 28;2021:8852574. doi: 10.1155/2021/8852574. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34136574 Free PMC article.
-
The role of HIF-1α in hypoxic metabolic reprogramming in osteoarthritis.Pharmacol Res. 2025 Mar;213:107649. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2025.107649. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Pharmacol Res. 2025. PMID: 39947451 Review.
-
Pathological progression of osteoarthritis: a perspective on subchondral bone.Front Med. 2024 Apr;18(2):237-257. doi: 10.1007/s11684-024-1061-y. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Front Med. 2024. PMID: 38619691 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

