Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation (HAL) vs. Rubber Band Ligation (RBL) for Second- and Third-Degree Hemorrhoids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40161159
- PMCID: PMC11955090
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.79810
Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation (HAL) vs. Rubber Band Ligation (RBL) for Second- and Third-Degree Hemorrhoids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
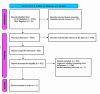
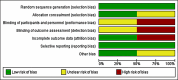
This systematic review investigates the outcomes of rubber band ligation (RBL) vs. hemorrhoidal artery ligation (HAL) for second and third-degree hemorrhoids. This review was designed, performed, and reported as per the recommendations of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. Literature databases, including PubMed, Cochrane, Science Direct, and Google Scholar, were searched for studies comparing rubber band ligation vs. hemorrhoidal artery ligation for second- and third-degree hemorrhoids. The primary outcome was the recurrence of hemorrhoids, while post-operative bleeding, post-operative pain, surgical site infection, and success rate were the secondary outcomes. The literature search and inclusion criteria identified five studies (n=953) comparing HAL (n=548) vs. RBL (n=405). The recurrence rate was higher in the RBL group (28.4%) compared to the HAL group (19.3%) (odds ratio {OR}: 0.57, p=0.001). The two groups showed comparable results regarding post-operative pain (OR: 0.77, p=0.77), post-operative bleeding (OR: 1.48, p=0.44), and surgical site infection (risk difference: 0.00, p=0.67). Moreover, the short-term success rate was 85% in HAL compared to 86% in RBL (p=0.71). Rubber band ligation and hemorrhoidal artery ligation showed comparable short-term outcomes regarding symptom treatment, post-operative bleeding, and pain. However, HAL was superior in terms of recurrence rate.
Keywords: 2nd and 3rd degree hemorrhoids; 2nd degree and 3rd degree haemorrhoids; hemorrhoidal artery ligation operation (halo); hemorrhoids surgery; proctology; rubber band ligation procedure.
Copyright © 2025, Abounozha et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures






References
-
- The prevalence, characteristics and treatment of hemorrhoidal disease: results of an international web-based survey. Sheikh P, Régnier C, Goron F, Salmat G. J Comp Eff Res. 2020;9:1219–1232. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
