This is a preprint.
Stress-dependent activation of PQM-1 orchestrates a second-wave proteostasis response for organismal survival
- PMID: 40161606
- PMCID: PMC11952446
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.11.642454
Stress-dependent activation of PQM-1 orchestrates a second-wave proteostasis response for organismal survival
Abstract
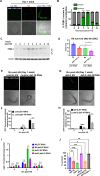
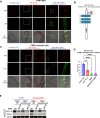
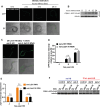
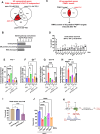
Stress responses are controlled by specialized stress-responsive proteostasis transcription factors that rapidly upregulate protein quality components to re-establish protein homeostasis and safeguard survival. Here we show that the zinc finger transcription factor PQM-1 is crucial for stress survival in response to thermal and oxidative challenges. We provide mechanistic insight into the regulation of PQM-1 during stress that depends on ILS-DAF-16 signaling, as well as phosphorylation on threonine residue 268 that is located within a conserved AKT motif. Our data show that in reproductively mature adults and during well-fed conditions, PQM-1 induction requires DAF-16 and occurs during the recovery period post heat shock. Moreover, PQM-1 co-localizes with DAF-16 in the nucleus during the stress recovery phase. This regulatory dependency on DAF-16 is bypassed under dietary restriction, allowing PQM-1 to promote stress resilience independent of the ILS pathway. During both conditions, PQM-1 is crucial for the upregulation of cytosolic and endoplasmic reticulum stress response genes required for organismal recovery and stress resilience. Our transcriptional and bioinformatic analysis reveals that PQM-1 regulates a distinct set of target genes during the stress recovery phase, suggesting that PQM-1 may be involved in vital secondary wave stress response. Thus, our findings uncover a previously unrecognized mechanism of stress-dependent PQM-1 activation that integrates multiple environmental cues to ensure proteostasis and organismal survival.
Figures
References
-
- Anckar J. & Sistonen L. Regulation of HSF1 function in the heat stress response: implications in aging and disease. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 80, 1089–1115 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Honda Y. & Honda S. The daf-2 gene network for longevity regulates oxidative stress resistance and Mn-superoxide dismutase gene expression in Caenorhabditis elegans. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 13, 1385–1393 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
