This is a preprint.
KLF4 promotes a KRT13+ hillock-like state in squamous lung cancer
- PMID: 40161723
- PMCID: PMC11952405
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.10.641898
KLF4 promotes a KRT13+ hillock-like state in squamous lung cancer
Abstract
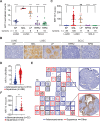
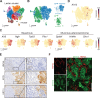
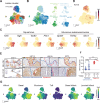
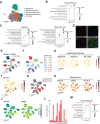
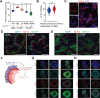
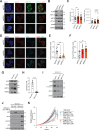
Lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) is basal-like subtype of lung cancer with limited treatment options. While prior studies have identified tumor-propagating cell states in squamous tumors, the broader landscape of intra-tumoral heterogeneity within LUSC remains poorly understood. Here, we employ Sox2-driven mouse models, organoid cultures, and single-cell transcriptomic analyses to uncover previously unrecognized levels of cell fate diversity within LUSC. Specifically, we identify a KRT13+ hillock-like population of slower-dividing tumor cells characterized by immunomodulatory gene expression signatures. The tumor hillock-like state is conserved across multiple animal models and is present in the majority of human LUSCs as well as head and neck and esophageal squamous tumors. Our findings shed light on the cellular origins of lung hillock-like states: normal club cells give rise to tumors with luminal hillock-like populations, while basal-like tumor-propagating cells transition into basal hillock-like states, resembling homeostatic cellular responses to lung injury. Mechanistically, we identify KLF4 as a key transcriptional regulator of the hillock-like state, both necessary and sufficient to induce KRT13 expression. Together, these results provide new molecular insights into cell fate plasticity that underlies intra-tumoral heterogeneity in LUSC, offering potential avenues for new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: KLF4; KRT13; cell fate; hillock; squamous lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS TGO has a patent related to SCLC subtypes and a sponsored research agreement with Auron Therapeutics, serves on the scientific advisory board (SAB) for Lung Cancer Research Foundation, and as a consulting editor for Cancer Research and Genes & Development. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures


References
-
- Ciriello G. et al. Cancer Evolution: A Multifaceted Affair. Cancer Discov 14, 36–48 (2024). 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-23-0530 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
