This is a preprint.
High-Density Multi-Distance fNIRS Enhances Detection of Brain Activity during a Word-Color Stroop Task
- PMID: 40161819
- PMCID: PMC11952576
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.12.642917
High-Density Multi-Distance fNIRS Enhances Detection of Brain Activity during a Word-Color Stroop Task
Update in
-
High-density multidistance fNIRS enhances detection of brain activity during a word-color Stroop task.Neurophotonics. 2025 Jul;12(3):035010. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.12.3.035010. Epub 2025 Sep 2. Neurophotonics. 2025. PMID: 40917100 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Significance: Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS) enables neuroimaging in scenarios where other modalities are less suitable, such as during motion tasks or in low-resource environments. Sparse fNIRS arrays with 30mm channel spacing are widely used but have limited spatial resolution. High-density (HD) arrays with overlapping, multi-distance channels improve sensitivity and localization but increase costs and setup times. A statistical comparison of HD and sparse arrays is needed for evaluating the benefits and trade-offs of HD arrays.
Aim: This study provides a statistical comparison of HD and sparse fNIRS performance to inform array selection in future research.
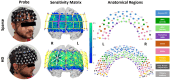
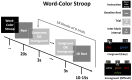
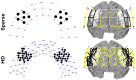
Approach: We measured prefrontal cortex (PFC) activation during congruent and incongruent Word-Color Stroop (WCS) tasks using both Sparse and HD arrays for 17 healthy adult participants, comparing dorsolateral PFC channel and image results at the group level.
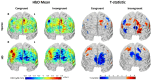
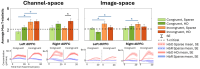
Results: While both arrays detected activation in channel space during incongruent WCS, channel and image space results demonstrated superior localization and sensitivity with the HD array for all WCS.
Conclusions: Sparse channel data may suitably detect activation from cognitively demanding tasks, like incongruent WCS. However, the HD array outperformed Sparse in detecting and localizing brain activity in image space, particularly during lower cognitive load tasks, making them more suitable for neuroimaging applications.
Keywords: Diffuse Optical Tomography; High-Density fNIRS; Pre-Frontal Cortex; Word-Color Stroop; fNIRS.
Conflict of interest statement
6DISCLOSURES The authors declare that there are no financial interests, commercial affiliations, or other potential conflicts of interest that could have influenced the objectivity of this research or the writing of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Ferrari M, Quaresima V. A brief review on the history of human functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) development and fields of application. Neuroimage. Academic Press; 2012. Nov 1;63(2):921–935. - PubMed
-
- Ehlis AC et al. Application of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in psychiatry. Neuroimage. Academic Press; 2014. Jan 15;85:478–488. - PubMed
-
- Chang F, et al. Research progress of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in patients with psychiatric disorders. https://doi.org/101080/2096179020201720901 [Internet]. Taylor & Francis; 2020. [cited 2021 Dec 7];6(2):141–147. Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/20961790.2020.1720901 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
